Abstract
We isolated endophytic fungi from the leaves of the conifer Juniperus chinensis var. sargentii inhabiting Mt. Hallasan. The fungal isolates were identified based on phylogenetic analysis using nucleotide sequences of the internal transcribed spacer region, large subunit region of ribosomal DNA, translation elongation factor, and β-tubulin region. In this study, we confirmed four species of unreported endophytic fungi in Korea, Allantophomopsis lycopodina, Epicoleosporium ramularioides, Kabatina juniperi, and Seiridium podocarpi. We describe their morphological characteristics and the results of the phylogenetic analysis.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Project on Survey and Discovery of Indigenous Fungal Species of Korea funded by NIBR of the Ministry of Environment and by the Project on Conservation and Adaptation of Forest Species Vulnerable to Climate Changes funded by National Arboretum of Korea Forest Service.
Figures & Tables
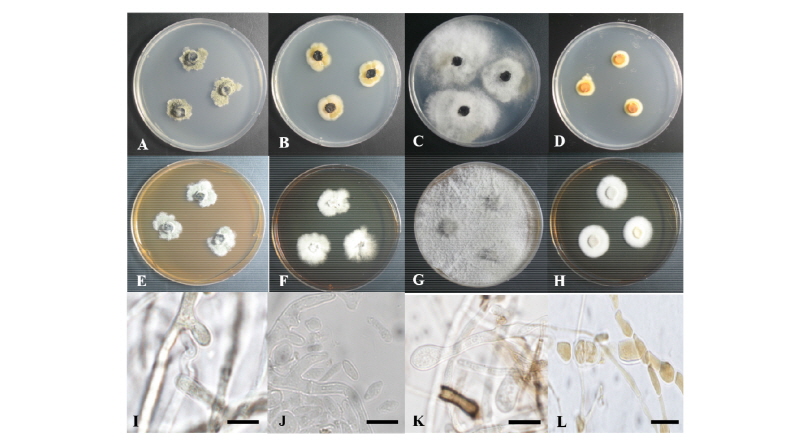
Fig. 1. Colonies of strain 17E013 (Epicoleosporium ramularioides) grown for 7 days on potato dextrose agar (PDA) (A) and malt extract agar (MEA) (E), conidiophore (I). Colonies of strain 17E062 (Kabatina juniperi) grown for 7 days on PDA (B) and MEA (F), conidia (J). Colonies of strain 17E063 (Allantophomopsis lycopodina) grown for 7 days on PDA (C) and MEA (G), conidiophore (K). Colonies of strain 17E066 (Seiridium podocarpi) grown for 7 days on PDA (D) and MEA (H), conidia (L) (scale bars =10 µm).


