Abstract
Selection of the optimal culture medium and evaluation of the antimicrobial activity against various phytopathogens were performed for four entomopathogenic fungal isolates with excellent insecticidal and antimicrobial activity against the two-spotted spider mite (Tetranychus urticae), green peach aphid (Myzus persicae), and gray mold (Botrytis cinerea). The optimal medium was selected by measuring the amount of blastospore production and the antifungal activity of the culture medium. On the basis of these experiments, GY medium was selected for Beauveria bassiana 2R-3-3-1 and Metarhizium anisopliae 4-2, SD3, and PDB medium for B. bassiana SD15. The antimicrobial activity test against other phytopathogens indicated that all four isolates showed high antifungal activities against Colletotrichum acutatum and Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. However, for Phytophthora capsici and C. fructicola, only M. anisopliae SD3 showed a high antifungal activity against P. capsici, and the other three isolates had little activity. Antibacterial activity against Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis was high in two isolates of M. anisopliae but not in two isolates of B. bassiana. Thus, it was confirmed that entomopathogenic fungi effective for pest control could be effectively used as a control agent for various plant diseases.
Figures & Tables
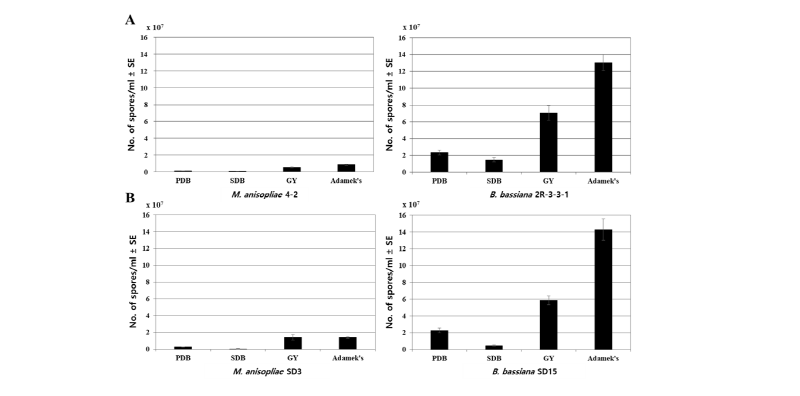
Fig. 1. Comparison of blastospore yields for 4 entomopathogenic fungi by each medium. A, mitepathogenic fungi; B, aphid-pathogenic fungi. Vertical bars correspond to standard error (SE).


