Abstract
We investigated the biodiversity of endophytic fungi in
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Project on Survey and Discovery of Indigenous Fungal Species of Korea funded by NIBR of the Ministry of Environment.
Figures & Tables
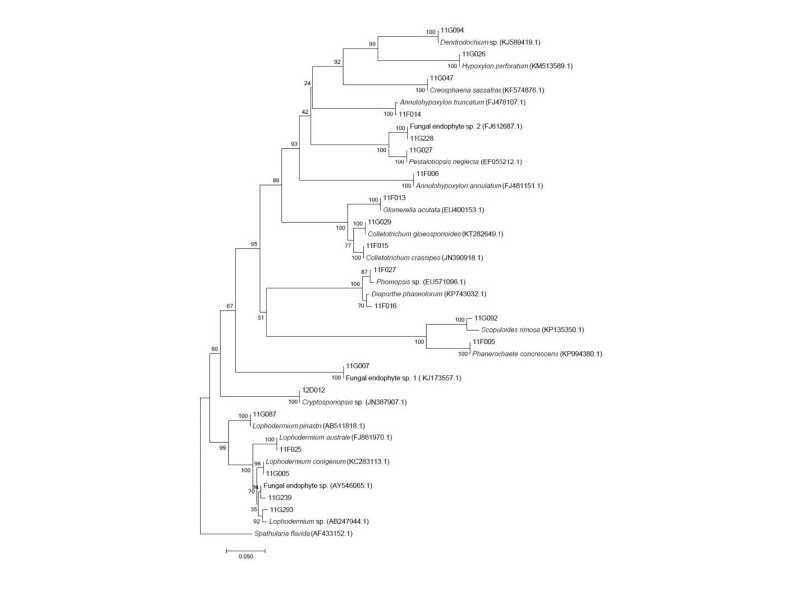
Fig. 1. Neighbor-joining phylogenic tree of endophytic fungi from and Junipreus rigida in Mt. Baekryeonsan and Johangsan. Internal transcribed spacer regions were used these sequence analysis to confirm the topological appropriation of isolates (1,000 replicates). was used as an out-group.


