Introduction
효모는 단일세포를 가지는 균계에 속하는 진핵생물 중 하나로 지금까지 1,500여종이 알려져 있다[1]. 효모의 크기는 일반적으로 직경 3-4 µm로 종과 환경에 따라 다르며 대부분의 효모는 출아법으로 번식하지만 세포분열을 하는 종도 있다. 일부 종은 균사가 자라는 곰팡이와 같이 의균사를 형성한다. 대부분 전통 발효식품 등에서 분리되어 산업적으로 이용되고 있다.
담수생태계에서 존재한다고 알려진 효모로는 Candida, Cryptococcus, Pichia, Rhodotorula 속 등이 주로 존재하며, 종 수준에서는 Aureobasidium pullulans, Cryptococcus albidus, Cr. laurentii, Debaryomyces hansenii, Rhodotorula mucilaginosa 등이 주로 보고되어 있다[2]. Pichia membranifaciens[3,4], Candida vartiovaarae[5], Debaryomyces hansenii[6]는 높은 농도의 NaCl이 포함된 환경에서도 생장이 가능하여 내염성을 가진다.
본 연구에서는 국내 담수 환경의 물과 토양, 침전식물체에서 야생효모를 분리 및 동정하여 효모의 종 다양성을 확인하고 이들 중 국내 미기록 효모 7종을 선별하여 종 특성을 알아보았다.
강원도 태백시, 속초시 및 충청북도 보은군, 전라북도 진안군의 담수지역에서 담수시료, 담수침전식물체, 담수퇴적물을 채집하여 야생효모를 분리하였다. 조사지점의 담수시료를 50 mL 채취하여 현장에서 핸드펌프와 nitrocellulose membrane filter (pore size 0.45 µm MCE membrane, MF-MilliporeTM, Burlington, MA, USA)를 이용하여 여과하였다. 필터의 상면을 water agar (WA, 20 g/L, agar)에 부착하여 15℃ 1일간 배양 후, membrane filter를 제거하고 실체현미경(Stemi 305, Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany)을 이용하여 발아한 포자를 배지에서 분리하고 V8한천배지(V8A; 8% V8 juice [v/v] and 1.5% agar [w/v] adjusted to pH6.0 using 10 N NaOH)에 배양하였다. 채집한 담수침전식물체는 멸균수에 2번 세척한 후 pretreatment liquid medium (0.05% 3-morpholinopropane-1-sulfonic acid (w/v), 0.05% KNO3 [w/v], 0.025% KH2PO4 [w/v], and 0.025% K2HPO4 [w/v])에 넣고 20℃에서 2일동안 배양한 후, 배양된 배지 100 µL를 WA에 도말하고 2일동안 15℃에서 배양하였다. 채집된 토양시료는 101, 102, 103으로 희석하여 50 ppm의 항생제(streptomycin, Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany)가 첨가된 potato dextrose agar (PDA, Difco, Detroit, MI, USA)에 도말한 후 3-4일 동안 15℃에서 배양하였다. 배양된 배지에서 단포자 분리를 통해 야생효모를 V8 한천배지에 순수분리하였다. 분리한 효모 확보를 위하여 yeast extract peptone dextrose broth (YPDB, Difco, Detroit, MI, USA)에 agar를 첨가한 yeast extract peptone dextrose agar (YPDA)배지를 만들어 계대배양하였다. 분리 효모의 포자를 관찰하기 위해 광학현미경(H550S, Nikon, Tokyo, Japan)을 이용하여 화상자료를 확보하였다.
이들 분리 효모들의 26S rDNA의 D1/D2 부위의 염기서열을 분석하기 위해 NL1(5’-GCATATCAATAAGCGGAGGAAAAG-3’)/NL4(5’-GGTCCGTGTTTCAAGACGG-3’) primer를 이용하여 결정한 후 NCBI의 BLAST를 사용하여 데이터베이스상의 기등록 효모들과의 상동성을 비교하였다. 계통수 작성은 MEGA7을 이용하였다[7].
환경조건에 따른 생장률을 조사하기 위해 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40℃의 6개 온도 범위와 pH 4-8의 5개 pH 범위의 YPDB, 5%, 15% NaCl (sodium chloride [w/v])을 첨가한 YPDB, 10%, 20% glucose [w/v]를 첨가한 YPDB, yeast vitamin free base (YVB, Formedium ltd., Hustanton, England), yeast mold broth (YMB, Difco, Detroit, MI, USA), potato dextrose broth (PDB, Difco, Detroit, MI, USA) 배지를 실험에 사용하였다[8]. 각각의 배지를 250 mL 삼각플라스크에 50 mL 조제하여 48시간 25℃, 250 rpm 진탕배양한 후 흡광도(600 nm, microplatereader Epoch2, Bioteck, Winooski, Vermont, USA)를 측정하였다.
Taxonomy
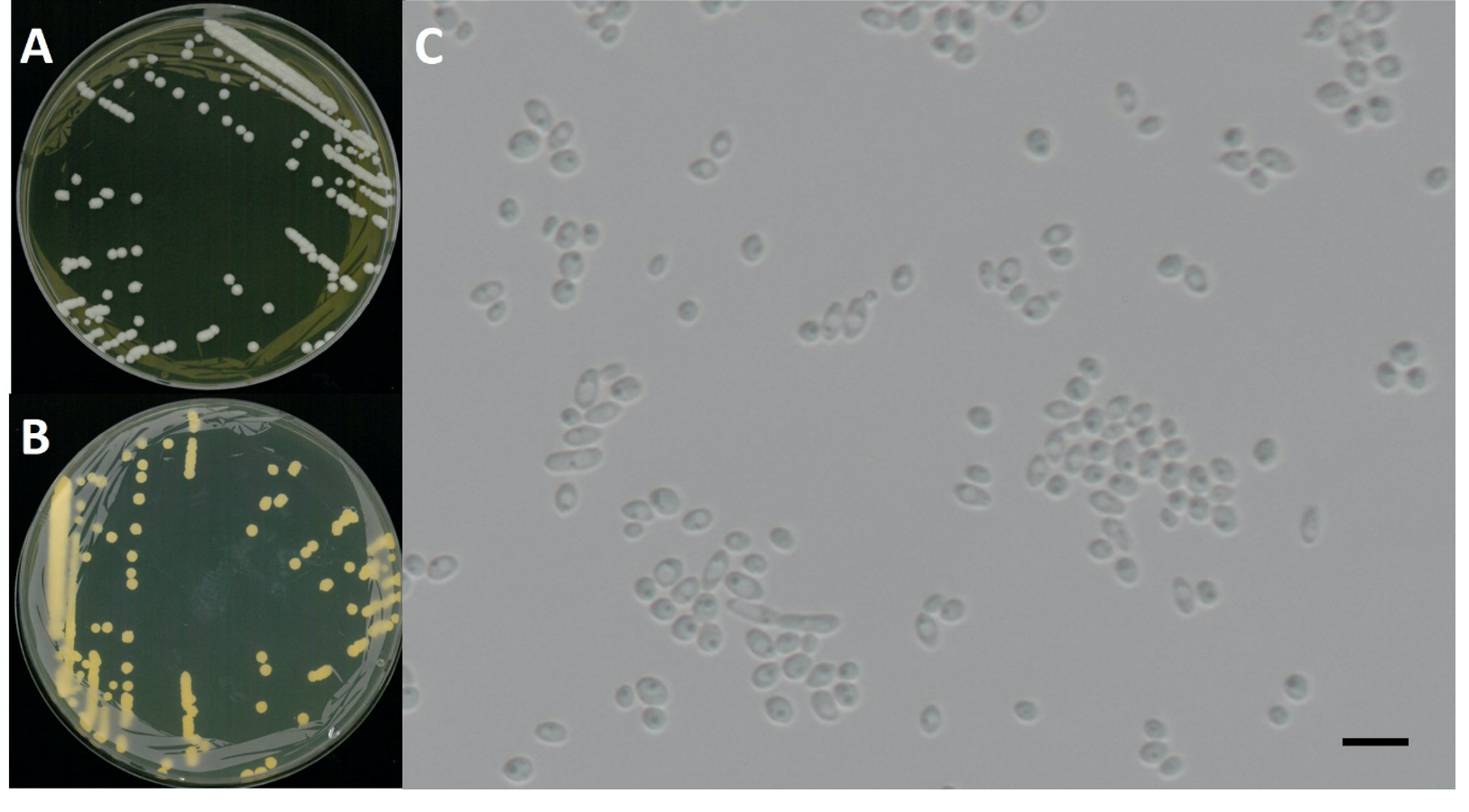
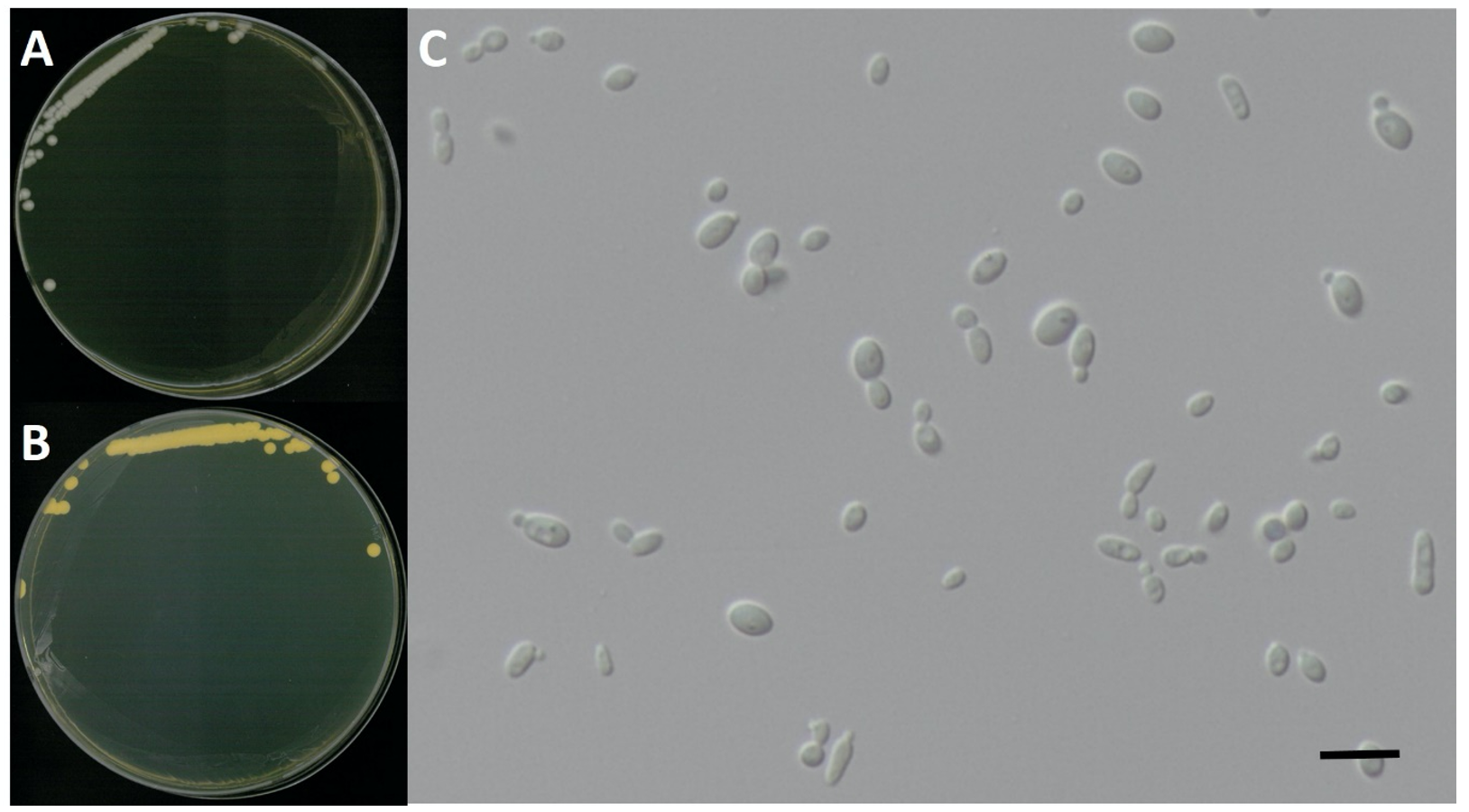
Pichia membranifaciens E.C. Hansen, Zentralblatt für Bakteriologie und Parasitenkunde, Abteilung 2 12: 538 (1904) [MB#227217] (Fig. 1 and 2; Table 1)
Characterization: YPDA 배지에서 25℃, 5일 동안 배양하였을 때 콜로니색은 전체적으로 흰색을 띄었다. 포자는 타원형으로 자낭포자와 의균사의 형성이 관찰되지 않았으며, 출아에 의한 무성생식을 하였다. 포자의 크기는 폭은 2.8 μm × 길이 4.4 μm이다. 5% NaCl을 함유한 YPDB배지에서 생육하는 호염성 효모이고 생육 온도는 20-35℃, 생육 pH는 4.0-8.0의 범위에서 잘 생장하였다.
Habitat: 석호의 담수퇴적물
Specimen examined: 강원도 속초시 청초호, 2017.01.23., NNIBRFG3732, 국립낙동강생물자원관
Note: NNIBRFG3732 균주(MT995084)는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI에서 blast한 결과, P. membranifaciens MUT63516 (MT151656) 균주와 100%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 P. membranifaciens (U75725)와 같은 clade에 묶이는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 P. membranifaciens로 동정되었다.
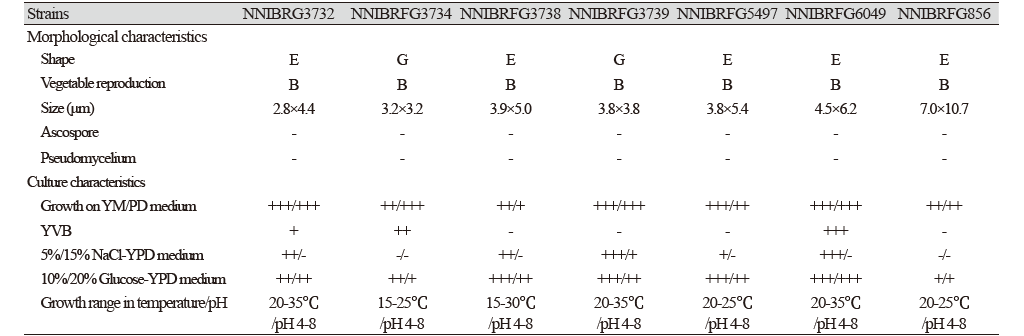
Candida vartiovaarae (Capr.) Uden & H.R. Buckley, Mycotaxon 17: 298 (1983) [MB#310354] (Fig. 1 and 3; Table 1)
Characterization: YPDA 배지에서 25℃, 5일 동안 배양하였을 때 콜로니색은 전체적으로 흰색을 띄었다. 포자의 형태는 구형으로 자낭포자와 의균사의 형성이 관찰되지 않았다. 출아에 의한 무성생식을 하였으며, 크기는 폭 3.2 μm × 길이 3.2 μm이다. 생육 온도는 15-25℃, 생육 pH는 4.0-8.0의 범위에서 잘 생장하였다. YVB에서도 잘 생장하였다.
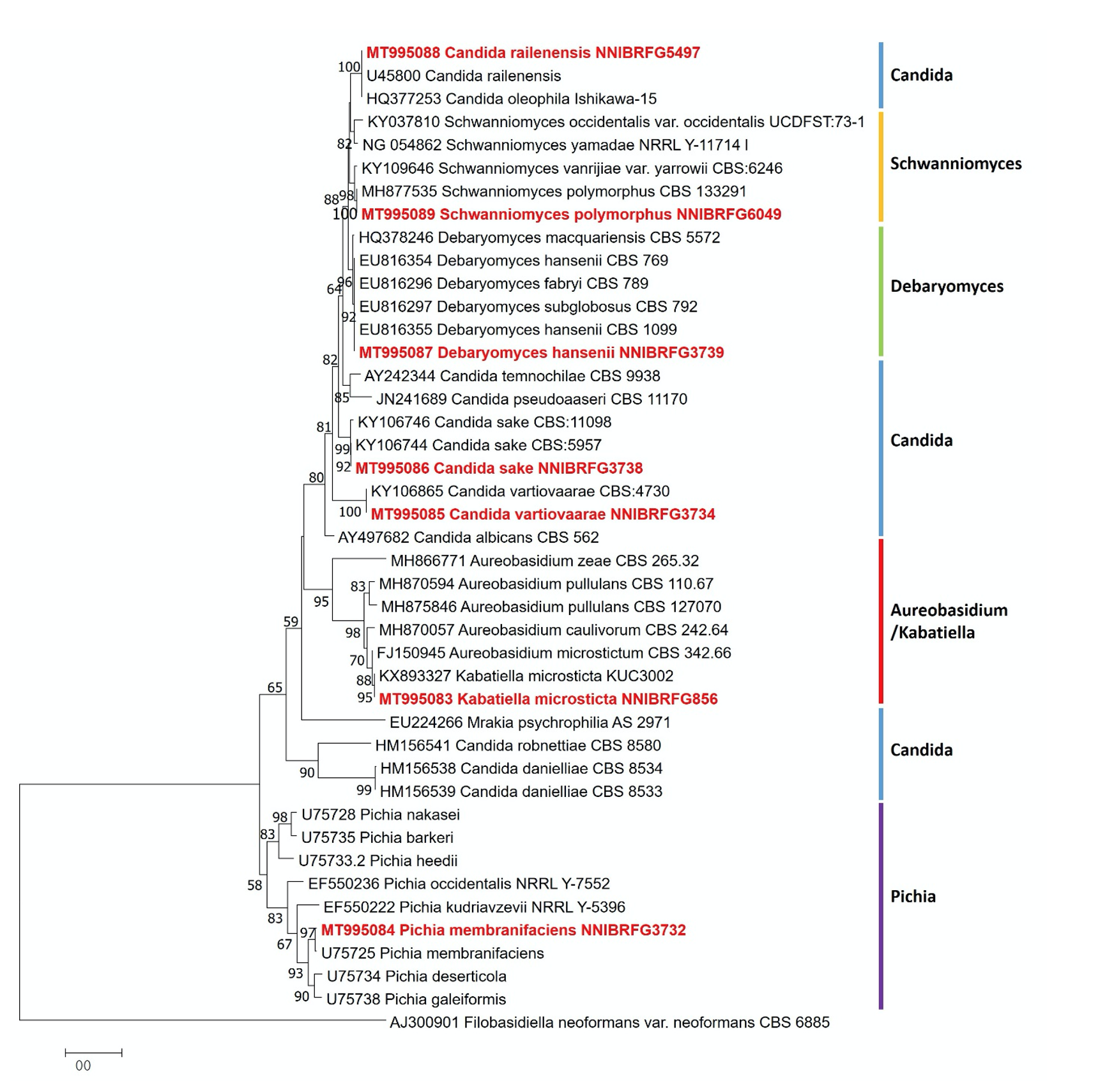
Fig. 1.Phylogenetic tree of Pichia membranifaciens NNIBRFG3732, Candida vartiovaarae NNIBRFG3734, C. sake NNIBRFG3738, C. railenensis NNIBRFG5497, Debaryomyces hansenii NNIBRFG3739, Schwanniomyces polymorphus NNIBRFG6049, Kabatiella microsticta NNIBRFG856 and related species based on a Neighbor-joining analysis of 26S rDNA sequences. The sequence of Filobasidiella neoformans var. neoformans was used as an outgroup. Numbers at the nodes indicate the bootstrap values (>50%) from 1,000 replications. The bar indicates the number of substitutions per position. The new isolates from the present study are shown in bold and red.
Habitat: 석호의 담수퇴적물
Specimen examined: 강원도 속초시 청초호, 2017.01.23., NNIBRFG3734, 국립낙동강생물자원관
Note: NNIBRFG3734 균주(MT995085)는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI에서 blast한 결과, C. vartiovaarae EXF-7987 (LT594913) 균주와 100%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 C. vartiovaarae CBS 4730 (KY106865)와 같은 clade에 묶이는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 C. vartiovaarae로 동정되었다.
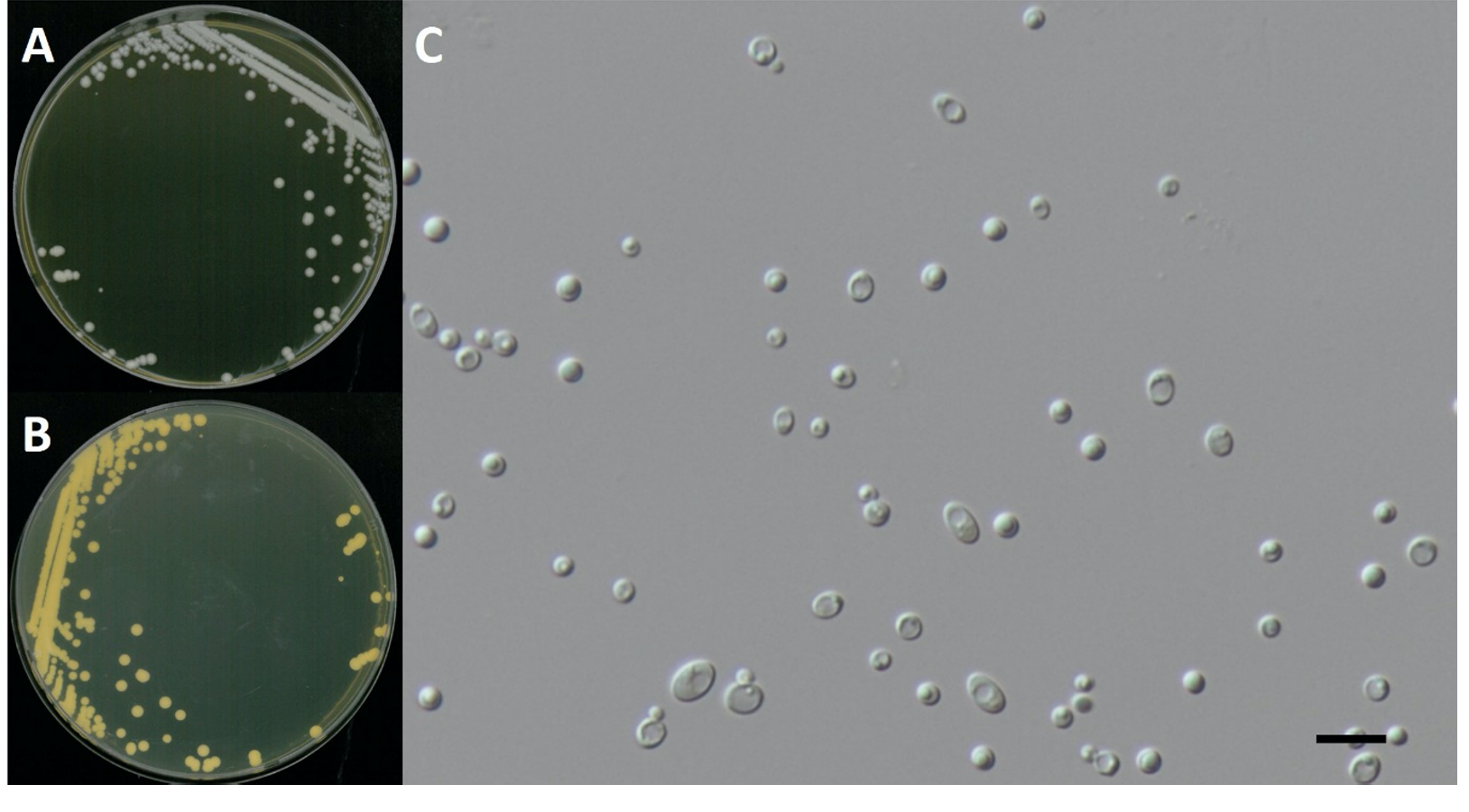
Candida sake (Saito & Oda) van Uden & H.R. Buckley, Mycotaxon 17: 298 (1983) [MB#283382] (Fig. 1 and 4; Table 1)
Characterization: YPDA 배지에서 25℃, 5일 동안 배양하였을 때 콜로니색은 전체적으로 흰색을 띄었다. 포자의 형태는 타원형으로 자낭포자와 의균사를 형성하지 않았다. 출아에 의한 무성생식을 하였으며, 크기는 폭 3.9 μm × 길이 5.0 μm이다. 5% NaCl을 함유한 YPDB배지에서 생육하는 호염성 효모이고 생육 온도는 15-30℃, 생육 pH는 4.0-8.0으로 넓은 범위의 pH에서 잘 생장하였다.
Habitat: 석호의 담수퇴적물
Specimen examined: 강원도 속초시 청초호, 2017.01.23., NNIBRFG3738, 국립낙동강생물자원관
Note: NNIBRFG3738 균주(995086)의 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI에서 blast한 결과, C. sake PYCC 2776 (MT577809) 균주와 100%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 C. sake CBS11098 (KY106744)과 같은 clade에 묶이는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 C. sake로 동정되었다.
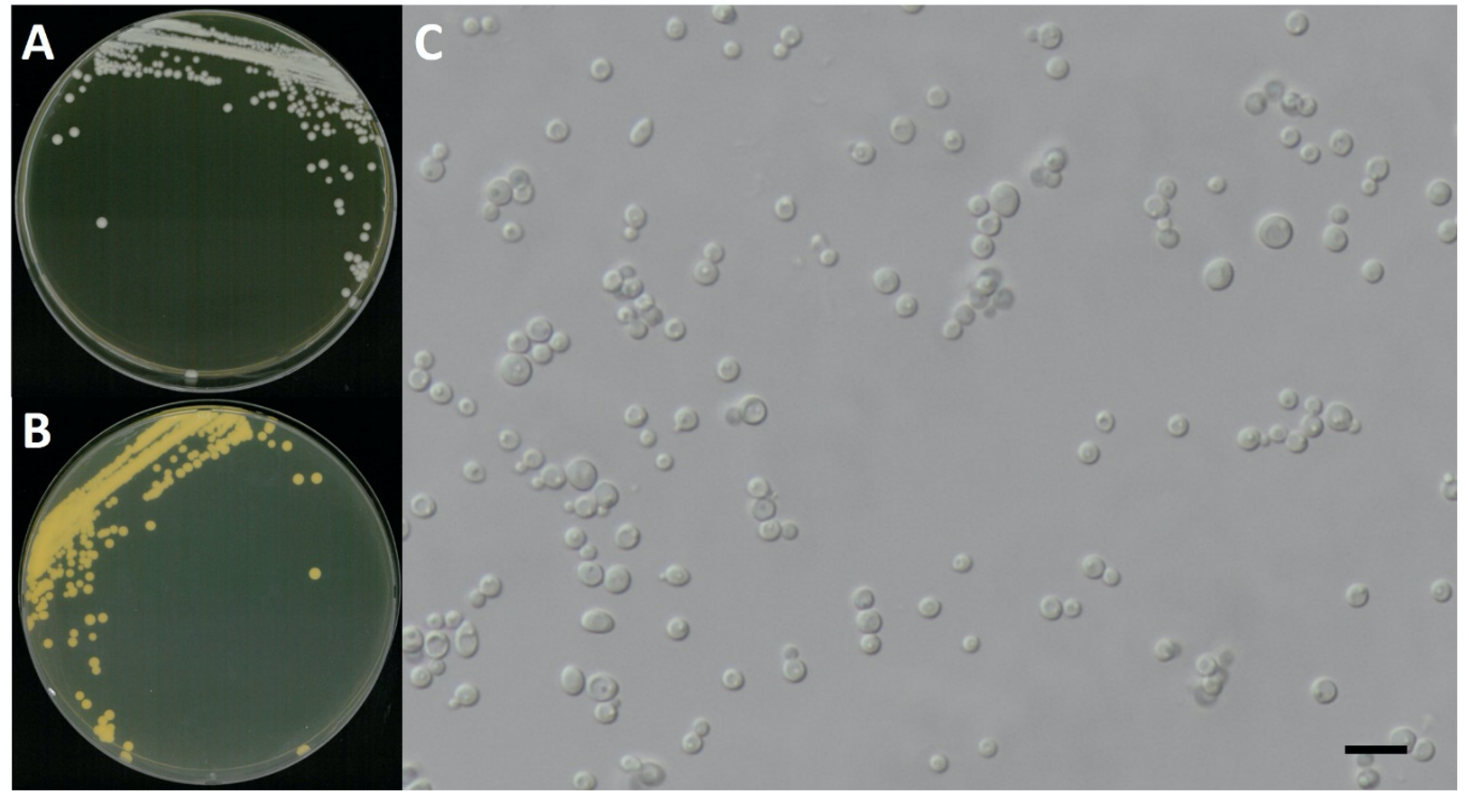
Candida railenensis C. Ramírez & A.E. González, Mycopathologia 88 (1): 55 (1984) [MB#105982] (Fig. 1 and 5; Table 1)
Characterization: YPDA 배지에서 25℃, 5일 동안 배양하였을 때 콜로니색은 전체적으로 흰색을 띄었다. 포자의 형태는 타원형으로 자낭포자는 관찰하지 못했으나 의균사의 형성은 관찰되었다. 출아에 의한 무성 생식을 하였으며, 포자의 크기는 폭은 3.8 μm × 길이 5.4 μm이다. 생육 온도는 20-25℃, 생육 pH는 4.0-8.0 범위에서 잘 생장하였다.
Habitat: 하천의 여과한 물
Specimen examined: 충청북도 보은군 보청천, 2018.03.09., NNIBRFG5497, 국립낙동강생물자원관
Note: NNIBRFG5497 균주(MT995088)는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI에서 blast한 결과, C. railenensis CBS 8177 (KY106717) 균주와 100%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 C. railenensis (U45800)와 같은 clade에 묶이는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 C. railenensis로 동정되었다.
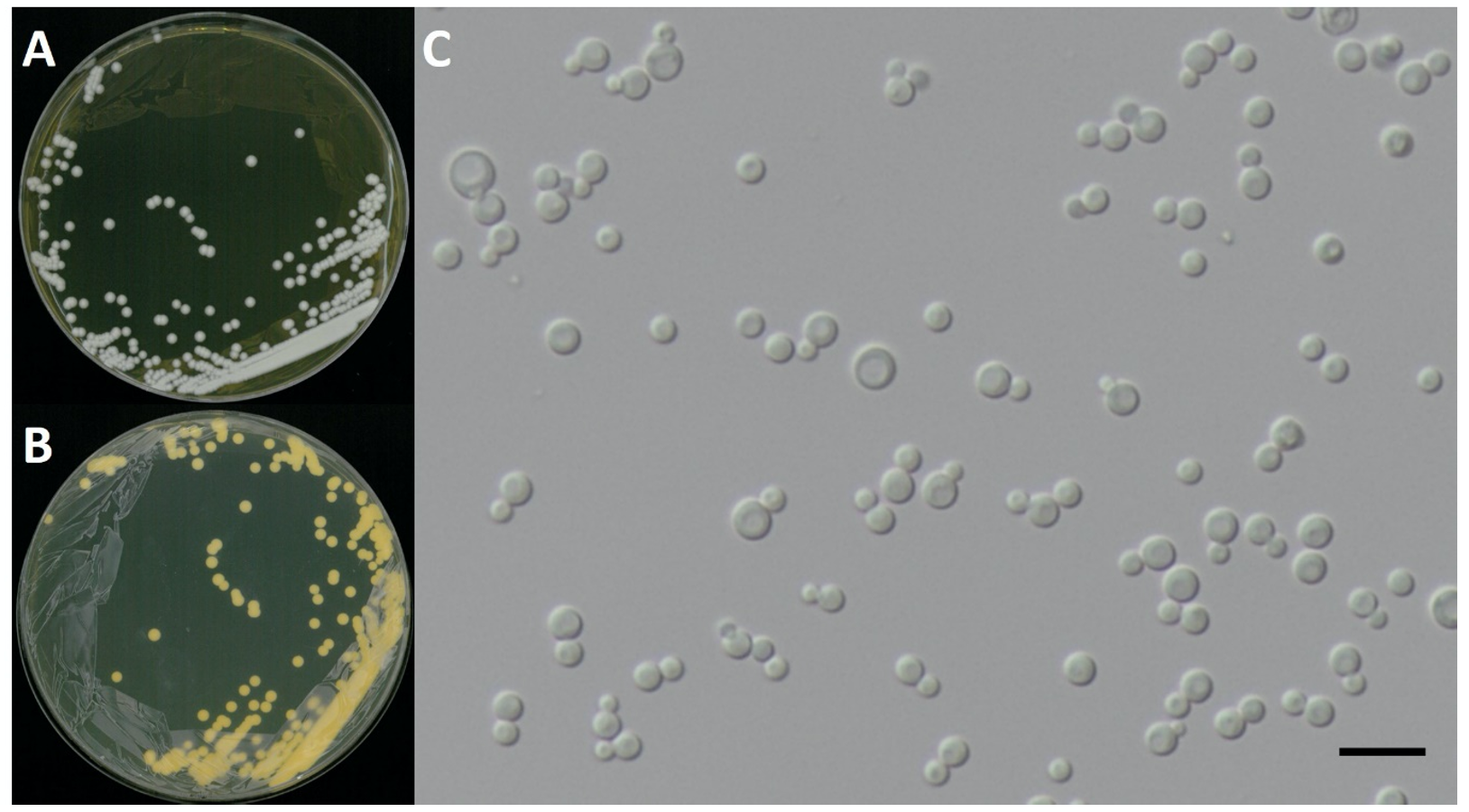
Debaryomyces hansenii (Zopf) Lodder & Kreger, The Yeasts: a taxonomic study: 280 (1952) [MB#296478] (Fig. 1 and 6; Table 1)
Characterization: YPDA 배지에서 25℃, 5일 동안 배양하였을 때 콜로니색은 전체적으로 흰색을 띄었다. 포자의 형태는 구형으로 자낭포자와 의균사의 형성이 관찰되지 않았다. 출아에 의한 무성 생식을 하였으며, 크기는 폭 3.8 μm × 길이 3.8 μm이다. 15% NaCl을 함유한 YPDB배지에서 생육하는 호염성 효모이고, 온도는 20-35℃, 생육 pH는 4.0-8.0의 범위에서 잘 생장하였다.
Habitat: 석호의 담수퇴적물
Specimen examined: 강원도 속초시 청초호, 2017.01.23., NNIBRFG3739, 국립낙동강생물자원관
Note: NNIBRFG3739 균주(MT995087)는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI에서 blast한 결과, D. hansenii 26IA4 (MT552613) 균주와 100%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 D. hansenii CBS796 (EU816354)와 같은 clade에 묶이는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 D. hansenii로 동정되었다.
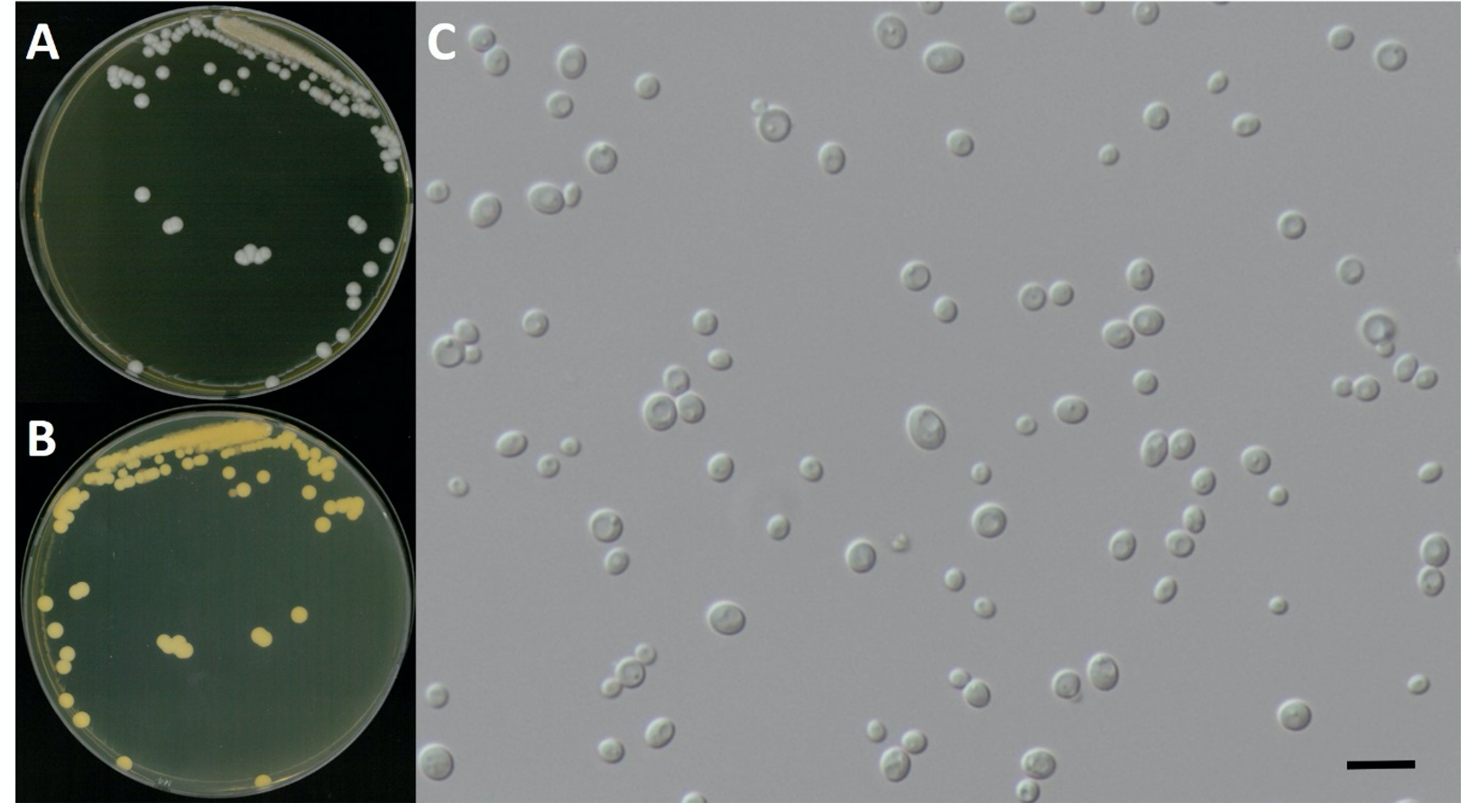
Schwanniomyces polymorphus (Klöcker) M. Suzuki & Kurtzman, Mycoscience 51 (1): 11 (2010) [MB#513478] (Fig. 1 and 7; Table 1)
Characterization: YPDA 배지에서 25℃, 5일 동안 배양하였을 때 콜로니색은 전체적으로 흰색을 띄었다. 포자의 형태는 타원형으로 자낭포자와 의균사의 형성이 관찰되지 않았다. 출아에 의한 무성 생식을 하였으며, 크기는 폭 4.5 μm × 길이 6.2 μm이다. 5% NaCl을 함유한 YPDB배지에서 생육하는 호염성 효모이고 생육 온도는 20-35℃, 생육 pH는 4.0-8.0의 범위에서 잘 생장하였다. YVB배지에서도 잘 생장하였다.
Habitat: 호수의 여과한 물
Specimen examined: 전라북도 진안군 용담호, 2018.06.21., NNIBRFG6049, 국립낙동강생물자원관
Note: NNIBRFG6049 균주(MT995089)는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI에서 blast한 결과, S. polymorphus CBS 133291 (MH877535) 균주와 100%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 같은 clade에 묶이는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 S. polymorphus로 동정되었다.
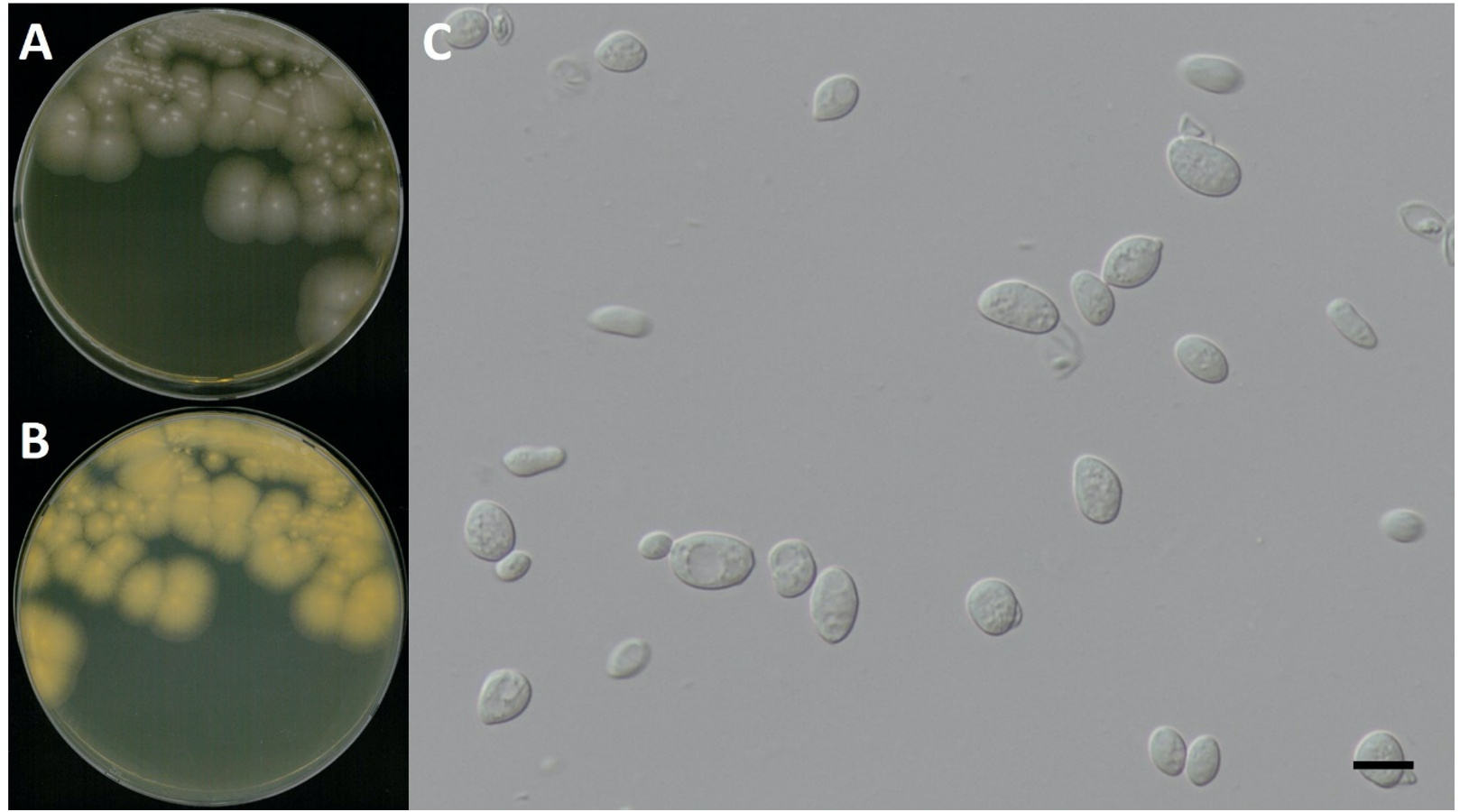
Kabatiella microsticta W.B. Cooke, Mycopathologia et Mycologia Applicata 17(1):1-43 [MB#326821] (Fig. 1 and 8; Table 1)
Characterization: YPDA 배지에서 25℃, 5일 동안 배양하였을 때 콜로니색은 전체적으로 연한 분홍색을 띄고 느리게 생장하였다. 포자의 형태는 타원형으로 자낭포자와 의균사를 형성하지 않았고 출아에 의한 무성 생식을 하였으며, 포자의 크기는 폭은 7.0 μm × 길이 10.7 μm이다. 생육 온도는 20-25℃, 생육 pH는 4.0-8.0의 범위에서 잘 생장하였다.
Habitat: 연못의 담수침전식물체
Specimen examined: 강원도 태백시 검용소, 2016.02.03., NNIBRFG856, 국립낙동강생물자원관
Note: NNIBRFG856 균주(MT995083)는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI에서 blast한 결과, K. microsticta LHX-B(MT107181) 균주와 100%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 K. microsticta KUC3002(KX893327)와 같은 clade에 묶이는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 K. microsticta로 동정되었다.