Abstract
Sclerotinia rot symptoms were observed in stringy stonecrop (
Figures & Tables
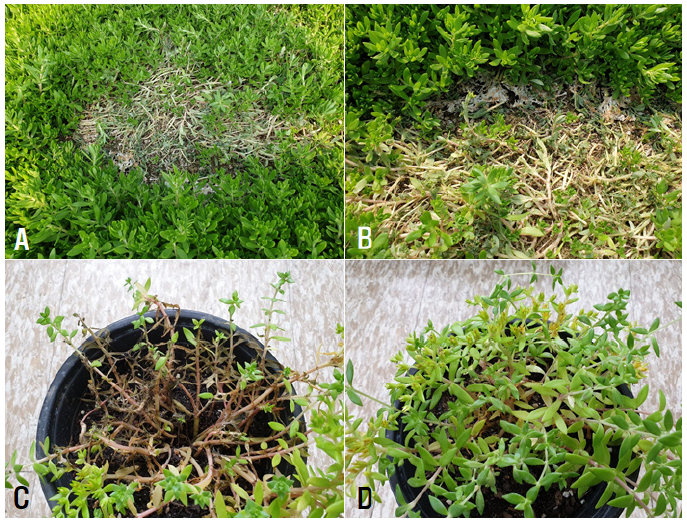
Fig. 1.Sclerotinia rot symptoms in stringy stonecrop plants. Symptoms observed in the vinyl greenhouses investigated (A and B). Symptoms induced by artificial inoculation test with an isolate of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (C). A non-inoculated plants (D).


