INTRODUCTION
The genus Plectosphaerella was established by Klebahn [1] to contain Plectosphaerella cucumeris Klebahn isolated from young cucumber plants in Germany. Recently, a new family named Plectosphaerellaceae W. Gams, Summerbell, and Zare has been introduced to include Plectosphaerella, Acrostalagmus, Gibellulopsis, Musicillium, and Verticillium [2]. Plectosphaerella has been recommended as the approved generic name in former publications rather than its anamorphic name Plectosporium Palm et al. [3]. Species in the genus Plectosphaerella are pathogenic towards several plant species, leading to fruit, root, and collar rot and collapse. Species such as P. cucumerina are mainly found in the soil or decayed plant material [4]. However, P. cucumerina has been infrequently described as a fungal pathogen on many crops, such as potato, tobacco, tomato, muskmelon, soybean, and pepper [4], or as endophytes inhabiting plant tissues without showing observable symptoms [5].
The asexual states of Plectosphaerella species are differentiated in terms of the proportion of conidial shape and dimensions, ratio of septate conidia, and presence or absence of chlamydospores [6-10] as well as internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region sequence data. However, significant distinction has been observed in the cultural and morphological characteristics between species in the genus Plectosphaerella [3, 10]. To describe species in this genus, sequences of the ITS region have been widely used, but large variations were observed in the ITS region of Plectosphaerella species [10]. Thus, multi-locus phylogenetic analysis based on the partial 28S rRNA gene, calmodulin, elongation factor 1-α, and β-tubulin gene was conducted to clarify species delimitations in Plectosphaerella [11]. In this study, we isolated an undescribed fungal species belonging to the genus Plectosphaerella, performed phylogenetic analysis, and described the morphological and cultural characteristics of this undescribed isolate.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Soil samples collection and fungal strains isolation
In 2017, a soil sample was collected from the field in Jeongeup, Jeollabuk-do, Korea (35°33'08.5"N, 126°52'05.5"E). The collected soil sample was air-dried and stored in a plastic bag at 4°C prior to use. A conventional dilution planting technique was applied to isolate the fungus [12]. One gram of soil sample was mixed with 10 mL of sterile distilled water. The suspension was vortexed and diluted, and a serially diluted sample was prepared. Subsequently, 100 µL of suspension was spread onto potato dextrose agar (Difco, Detroit, MI, USA).
Morphological observations
To examine the growth rate of the fungal colonies, the petri dishes were incubated at 25°C for 5 days. After 2~3 days, fungal colonies were isolated, and NC14-264 was selected among the isolated strains for subsequent analysis. To evaluate cultural and morphological characteristics, the fungal strain was incubated on potato dextrose agar (PDA), 2% malt extract agar (MEA), and oatmeal agar (OA) at 25°C for 10 days. Morphological structures were observed on OA media, measured, and photographed after 10 days under a light microscope (BX-50; Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). The NC14-264 isolate was deposited at the National Institute of Biological Resources as ZEVCFG0000000095.
DNA extraction, PCR amplification and Sequencing
On the PDA plate, total genomic DNA was extracted from the mycelia of a fungal strain NC14-264 using the HiGene Genomic DNA Prep kit (BIOFACT, Daejeon, Korea) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The primers LROR and LR5 [13] were used to amplify the partial 28S rRNA gene, and the ITS1F/ITS4 [14, 15] primer pair was used to amplify ITS region sequences. Amplifications were performed in an Applied Biosystems PCR machine using the following parameters: 94°C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles at 94°C for 40 sec, an annealing temperature dependent on the gene amplified (52°C for large subunit, 54°C for ITS) for 60 sec, and 72°C for 120 sec, with a final extension at 72°C for 10 min [11]. The amplified PCR fragments were purified using ExoSAP-IT (Affymetrix, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Finally, 503- and 566-bp ITS region and partial 28S rRNA gene sequences were obtained from NC14-264 and deposited in NCBI GenBank under accession numbers LC405939 and LC405940, respectively. Reference sequences were obtained from GenBank under the accession numbers shown in Table 1.
|
Table 1. A list of Plectosphaerella strain and reference strains of related species in this study 
|
|
|
ITS, internal transcribed spacer; LSU, large subunit. |
|
Phylogenetic analyses
For molecular analysis of this strain, the phylogenetic tree was constructed based on ITS region and partial 28S rRNA gene sequences using the maximum parsimony method by MEGA 6 software with a bootstrap of 1,000 replicates [16]. The identity of the isolate NC14-264 was confirmed by BLAST analysis, revealing 100% similarity to the partial 28S rRNA sequence of P. sinensis ACCC 39144 and 100% similarity to the ITS region sequence of P. sinensis ACCC 39145.
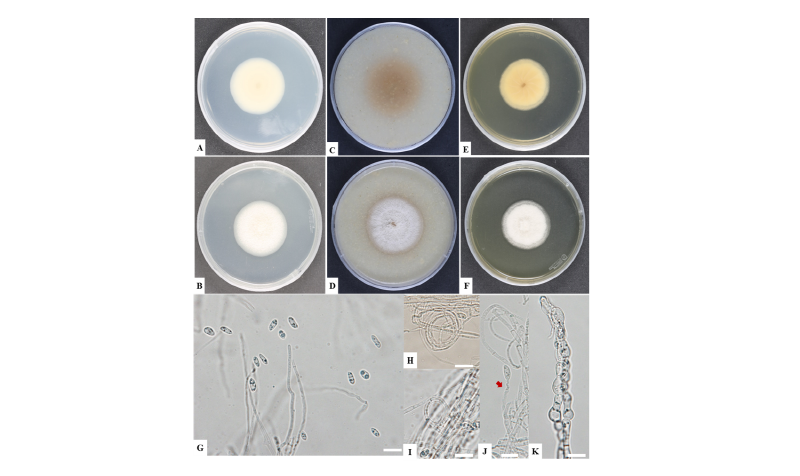
Fig. 1. Cultural and morphological characteristics of Plectosphaerella sinensis NC14-264. A, B, Colonies on potato dextrose agar; C, D, Colonies on oatmeal agar; E, F, Colonies on malt extract agar; G, conidia; H, I; Conidiophores from hyphal coils; J, Conidiophores (arrow denotes conidiophore); K, Chlamydospores (scale bars = 10 μm).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Phylogenetic results based on the combined ITS gene and partial 28S rRNA gene sequences revealed a clear separation between P. sinensis and other Plectosphaerella spp. [17]. In the phylogenetic tree, the representative isolate NC14-264 was clustered within a clade containing reference isolates of Plectosphaerella sinensis (Fig. 2).
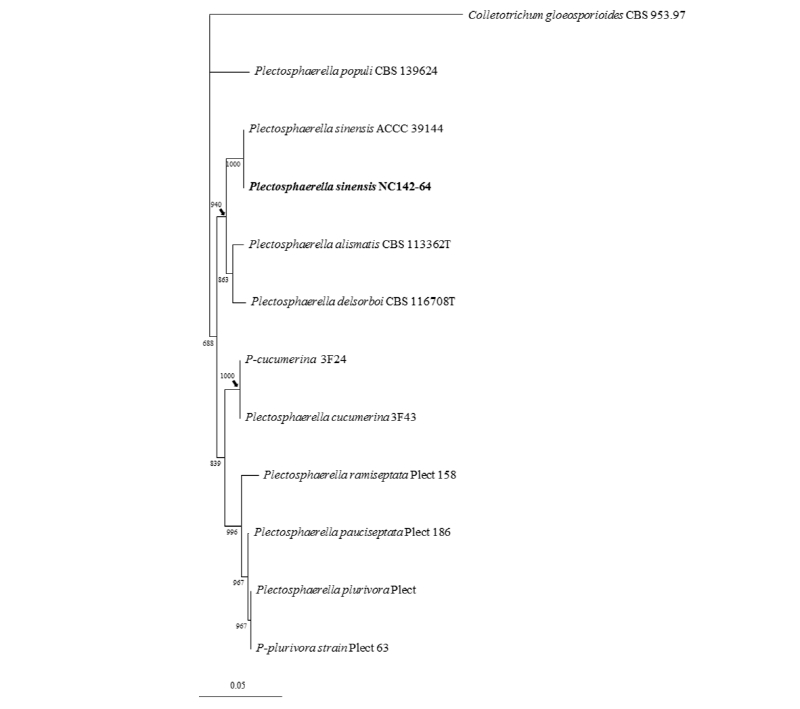
Fig. 2. One of the ten most parsimonious trees generated from maximum parsimony analysis of obtained sequences from the internal transcribed spacer region and the partial 28S rRNA genes. Colletotrichum gloeosporioides strain was used as an outgroup, and bootstrap values smaller than 80% were not shown. The fungal isolate used in this study is in bold. The scale bar indicates the number of nucleotide substitutions.
Taxonomic descriptions and microphotographs of morphological structures of the isolate NC14-264 are shown in Table 2 and Fig. 2. Colonies grew moderately, reaching 54 mm in diameter on PDA, 55 mm on OA, and 49 mm on MEA at 25°C for 10 days of incubation. Colonies on OA became buff, plane, and portioned with regular margins (Fig. 1C, 1D). Hyphae were colorless, septate, branched, and commonly 1.7~3.9 μm (mean = 2.4 μm) wide. Conidiophores, formed by hyphal coils or from prostrate hyphae developing on the surface of the media, were occasionally branched and solitary. Conidiogenous cells were phialidic, detached, determinate, and smooth with an indistinct collarette. They were also flask-shaped, normally widened at the bottom, solitary, hyaline-to-subhyaline, and 4.8~15.9 × 2.0~4.1 μm in size (mean = 12.2 × 2.4 μm). Conidia formed in smarmy heads on the upper part of the phialides and were ellipsoid with a slight apiculate base, 0~1-septate, smooth-to-finely coarsened, and 6.1~9.8 × 1.8~4.4 μm in size. Chlamydospores were terminal or intercalary, uneven, thick-walled, and 4.3~10.2 μm in diameter. The morphological and cultural characteristics of NC14-264 matched those of P. sinensis ACCC 39144 (Table 2).
Many species in genus Plectosphaerella are well-known as not only important pathogens of several plant species, causing fruit, root, and collar rot and collapse [18], but also as endophytes in symptomless plant tissue and soil [5]. Plectosphaerella species are distinguished based on the proportion of their conidial shape and dimensions, ratio of septate conidia, and presence or absence of chlamydospores [6-10]. Large differences have been observed in the cultural and morphological characteristics between species in the genus Plectosphaerella. [3, 10]. Plectosphaerella species are plant pathogens occupying mainly the plant parts, such as stems, roots, and leaves. However, our study revealed the occurrence and diversification of P. sinensis in soil. In a recent study [11], multi-gene phylogenetic analysis of the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) regions, calmodulin (CaM) genes, elongation factor 1-α (EF1) and part of beta-tubulin gene region (TUB) and morphological characteristics have been used to describe well-separated species of Plectosphaerella. In this study, however, the ITS region and partial 28S rRNA genes were useful to clearly distinguish among different species in this genus. However, further studies of Plectosphaerella species in Korea are needed to fully understand their occurrence, diversification, and characterization.


