서론
식물에 탄저병을 일으키는 Colletotrichum 속 진균은 과수와 채소 등 넓은 기주 범위를 갖고 있으며 작물의 잎, 줄기, 열매 등에 궤양과 부패 등의 증상을 일으켜 많은 경제적인 피해를 주고 있다[1, 2]. 수출 종자에서 검역대상이 되고 있는 탄저병균은 C. orbiculare, C. coccodes, C. circinans 등이 있고 C. orbiculare는 메론, 호박, 오이, 수박 같은 박과 작물에 병을 일으키고, C. coccodes는 토마토와 고추 등에 병을 일으키며 C. circinans는 양파에 병을 일으킨다[3-5]. 이러한 탄저병균은 종자에 부착하여 잠복할 가능성이 있어 국내외로 유입되어서 정착하여 피해를 주기 때문에 철저한 검역을 실시하고 있다. 검사 방법은 병징이 확인된 시료와 무작위로 선별된 시료를 대상으로 배지에 배양하여 현미경을 통하여 균사나 포자를 관찰하여 판명하였다. 또는 분자적 방법으로 internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region을 대상으로 염기서열을 분석하고 동정하여 판명하고 있다. 현미경 관찰로 판명하기에는 검사자 간의 숙련도나 주관에 따라 검사의 정확도가 영향을 많이 받아 정확한 검사로는 어려움이 있다. ITS region 염기서열 분석을 통한 동정은 진균의 염기서열 데이터가 점점 축적됨에 따라 다른 종의 진균에서 동일한 ITS region 염기서열이 존재함을 알게 되어 정확한 종 동정에 어려움이 나타났다. 그러므로 본 연구에서는 진균의 종간 염기서열이 차이가 많아 종 동정에 사용되는 housekeeping gene인 translation elongation factor 1-α (tef-1α) 유전자와 β-tubulin 유전자 염기서열을 비교 분석하여 탄저병의 원인균인 C. circinans의 특이 검출 마커를 개발함에 있다. 그리고 일반 PCR 방법과 real-time PCR 방법을 사용하여 검출 감도를 측정하고, 검역 현장이나 탄저병 발생 농장에 적용하여 빠른 검출을 위해 감염된 종자나 작물에서 신속하고 정확하게 검출 가능한 PCR 검출법을 개발함에 있다.
재료 및 방법
공시균주와 배양조건
본 연구에 사용된 Colletotrichum 속 균주들은 국립농업과학원 미생물은행(Korean Agricultural Culture Collection, KACC)에서 비교 분석할 Colletotrichum 12 종 20 strain을 분양 받았으며 KACC에서 보관중인 Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures-Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences Collections (CBS-KNAW)의 C. circinans 2 개 균주를 분양 받았다(Table 1). 그리고 농작물 또는 작물의 표면에 서식하는 부생균으로 흔하게 존재하는 Alternaria sp., Aspergillus sp., Cladosporium sp., Fusarium sp., Penicillium sp., Trichoderma sp. 6균주를 사용하였다. 모든 균주는 potato dextrose agar (PDA; Difco, Detroit, MI, USA) 배지에 25℃ 온도조건으로 10~14 일 동안 암조건에서 배양하였다.
C. circinans 특이 검출 PCR 마커 탐색 및 제작
Genomic DNA는 균주를 PDA 배지에 25℃에서 10 일간 암조건에서 배양한 후 DNeasy Plant mini kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA)를 사용하여 추출하였다[6, 7]. TEF728 (5′-CAT CGA GAA GTT CGA GAA G-3′)과 TEF1 primer (5′-GCC ATC CTT GGA GAG ATA CCA GC-3′)를 사용하여 PCR을 통해 tef-1α 유전자를 증폭하였고[8,9], T10 (5′-ACG ATA GGT TCA CCT CCA GAC-3′)과 BT12 (5′-GTT GTC AAT GCA GAA GGT CTC-3′)를 사용하여 β-tubulin 유전자를 증폭하였다[10, 11]. 증폭된 PCR 산물은 NAVIGen PCR Purification Kit (NAVIBIOTECH, Cheonan, Korea)를 사용하여 정제하고 Macrogen (Seoul, Korea)에 의뢰하여 염기서열을 분석하였다. 분석된 염기서열은 GenBank DNA database ()에서 유전자 염기서열을 확인하였다. Clustal Omega 프로그램 ()을 사용하여 분석한 염기서열을 나열하고 유사성을 비교 분석하였다. 종 간 차이가 나타나는 염기서열 부분을 바탕으로 C. circinans 특이 검출 마커를 각각 tef-1α 와 β-tubulin 유전자에서 디자인하였다.
PCR 마커의 C. circinans 특이성 검정
제작된 primer set들의 특이성 검정은 Table 1에 있는 모든 Colletotrichum종들의 strain과 종자 표면에 존재할 가능성이 큰 부생균인 Alternaria sp., Aspergillus sp., Cladosporium sp., Fusarium sp., Penicillium sp., Trichoderma sp. 6 가지 속의 진균에 대해서도 수행하였다. PCR 조건은 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set를 사용하였을 때, initial denaturation 95℃에서 3 분, denaturation 95℃에서 30 초, annealing 58℃에서 30 초, extension 72℃에서 30 초 순서로 25 회 반복 수행하고 마지막으로 72℃에서 5 분 반응하여 증폭하였으며, cirTu-F/cirTu-R set를 사용할 때에는 annealing을 50℃로 수행하였다. 반응이 끝난 PCR 산물은 1.5% agarose gel로 100 V, 25 분 동안 전기영동하여 DNA band와 그 size를 확인하였다.
일반 PCR 방법과 real-time PCR 방법을 이용한 C. circinans 검출 감도 분석
제작된 마커의 C. circinans 검출 감도를 분석하고자 C. circinans DNA를 10 ng/μL 농도로 정량하고 10 배씩 단계적으로 희석하여 10 ng, 1 ng, 100 pg, 10 pg, 1 pg, 100 fg, 10 fg, 1 fg의 DNA 농도를 PCR 반응의 주형 DNA로 사용하였다. 일반 PCR 방법으로는 EmeraldAmp GT PCR Master Mix (Takara Bio, Kusatsu, Japan)에 단계적으로 희석한 DNA를 주형으로 전체 50 μL로 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set와 cirTu-F/cirTu-R set를 앞서 서술한 PCR 조건으로 각각 수행하였다. 반응이 끝난 PCR 산물은 1.5% agarose gel로 100 V, 25 분 동안 전기영동하여 DNA band와 그 size를 확인하였다.
Real-time PCR 분석은 단계적으로 희석한 DNA를 주형으로 전체 부피 25 μL로 SYBR Premix Extaq (Takara Bio)에 각각 첨가하여 PCR 반응액을 만들었다[12]. Real-time PCR 반응 조건은 95℃에서 30 초 반응 후, 95℃에서 5 초와 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set는 58℃에서 30 초, cirTu-F/cirTu-R set는 50℃에서 30 초를 35 회 반복하였으며 Takara Thermal Cycler Dice Real Time System TP800을 사용하여 3 회 반복하여 실험을 수행하였고 TaKaRa DiceRealTime Single 소프트웨어를 사용하여 분석하였다.
C. circinans에 감염된 양파 종자에서의 검출 확인
검역 현장에 적용하기 위하여 양파 종자를 대상으로 C. circinans를 감염시켜 실험을 진행하였다. 양파 종자의 표면에는 소독제가 코팅되어 있기에 멸균 증류수를 사용하여 코팅된 소독제를 깨끗하게 씻어 내고 0.25% 차아염소산나트륨으로 표면 살균한 후 멸균 증류수로 남아있는 차아염소산나트륨을 2 회 세척하여 제거하였다[13]. PDA 배지에 C. circinans를 14 일간 25℃에서 암조건으로 전배양 하였다. PD broth에 표면 살균한 양파 종자 100 개와 전배양한 C. circinans 균사 디스크 10 개를 함께 넣어 3 일간 진탕배양(25℃, 200 rpm) 한 후, 4 일간 정치배양 하였다. 함께 배양한 종자를 꺼내어 육안으로 탄저병에 감염된 종자를 선별하여 실험에 사용하였다. DNeasy Plant mini kit를 사용하여 선별된 탄저병 감염 종자에서 DNA 추출하였고 앞서 수행한 일반 PCR 방법과 real-time PCR 방법을 통해 검출 능력을 조사하였다.
결과 및 고찰
C. circinans 특이 검출 마커 개발
Clustal Omega 프로그램을 사용하여 분석한 tef-1α 와 β-tubulin 유전자 염기서열을 alignment하여 유사성을 비교하였다. Colletotrichum종 간 염기서열이 많이 차이가 나는 부분을 찾아 tef-1α 유전자에서 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set를 디자인하였고 β-tubulin 유전자에서 cirTu-F/cirTu-R set를 디자인하였다. 제작된 특이 검출 마커는 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set는 253 bp, cirTef-F/cirTef-R set는 115 bp를 증폭할 수 있게 디자인하였다(Fig. 1, 2, Table 2).
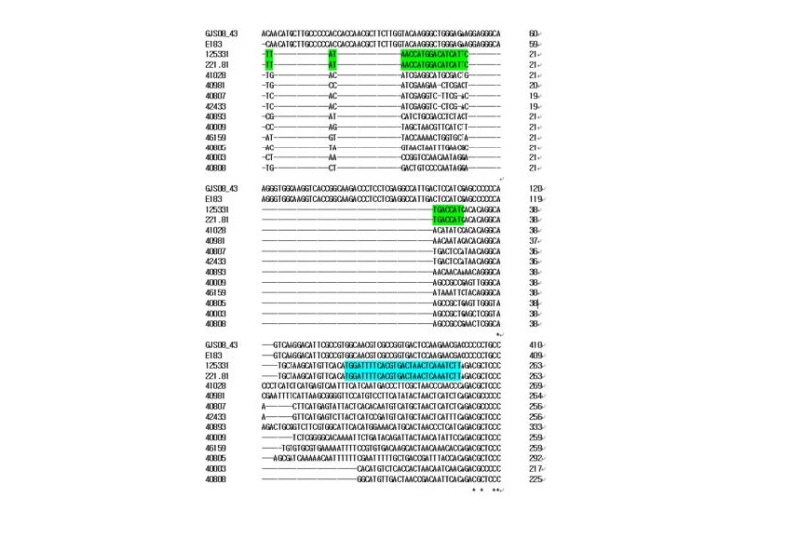
Fig. 1. Sequence alignment of translation elongation 1-α genes of Colletotrichum spp. used in this study. Green and sky-blue boxed sequences indicate respectively the position of the designed primer cirTef-F and cirTef-R. GJS08_43: C. theobromicola, E183: C. ignotum, 125331: C. circinans, 112.81: C. circinans, 41028: C. caudatum, 40807: C. higginsianum, 42433: C. lindemuthianum, 40893: C. boninense, 40009: C. coccodes, 46159: C. capsici, 40805: C. acutatum, 40003: C. gloeosporioides, 40808: C. orbiculare.
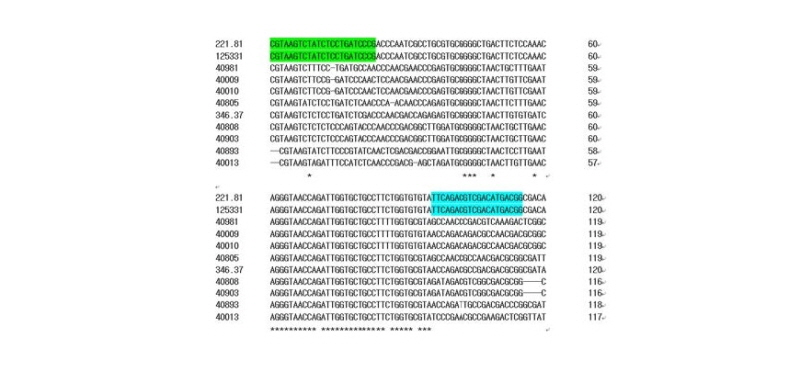
Fig. 2. Sequence alignment of β-tubulin genes of Colletotrichum spp. used in this study. Green and sky-blue boxed sequences indicate respectively the position of the designed primer cirTu-F and cirTu-R. 112.81: C. circinans, 125331: C. circinans, 40981: C. liliacearum, 40009: C. coccodes, 40010: C. coccodes, 40805: C. acutatum, 346.37: C. fructi, 40808: C. orbiculare, 40903: C. orbiculare, 40893: C. boninense, 40013: C. dematium.
C. circinans 검출 마커의 특이성 검정
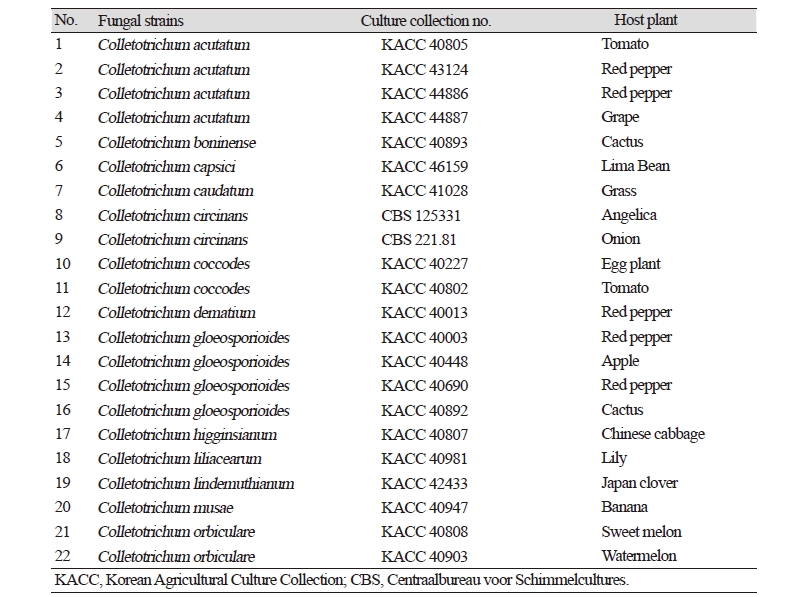
제작된 C. circinans 검출 마커인 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set와 cirTu-F/cirTu-R set를 각각 사용하여 C. circinans 2 개 균주를 포함하여 Colletotrichum 13 종, 22 strain과 부생균으로 존재하는 Alternaria sp., Aspergillus sp., Cladosporium sp., Fusarium sp., Penicillium sp., Trichoderma sp. 6 개 속 진균의 DNA를 주형으로 PCR을 수행하였다. 그 결과 C. circinans DNA에서만 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set를 사용하였을 경우 253 bp size의 band와 cirTu-F/cirTu-R set를 사용하였을 경우에는 115 bp size의 band를 확인하였고 다른 종의 Colletotrichum종에서는 band가 확인되지 않았다(Fig. 3, 4). C. circinans DNA와 6 개 속의 부생균의 DNA가 섞여 있을 경우에는 증폭이 잘 되었지만, 6 개 속 진균의 DNA만 섞여 있을 경우에는 증폭되지 않았다. 이 결과는 본 연구에서 제작한 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set와 cirTu-F/cirTu-R set 둘 다 C. circinans를 특이적으로 검출할 수 있다는 것을 보여준다.
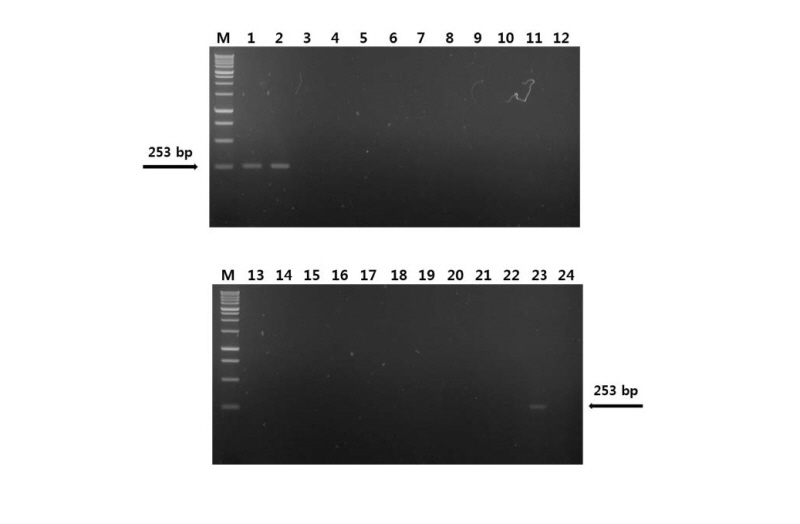
Fig. 3. Specificity test of the primer cirTef-F/cirTef-R set against diverse fungal DNAs. M, 1 kb DNA ladder; 1, Colletotrichum circinans CBS 125331; 2, C. circinans CBS 221.81; 3-6, C. acutatum KACC 40805, 43124, 44886, 44887; 7, C. boninense KACC 40893; 8, C. capsica KACC 46159; 9, C. caudatum KACC 41028; 10, 11, C. coccodes KACC 40227, 40808; 12, C. dematium KACC 40013; 13-16, C. gloeosporioides KACC 40003, 40448, 40690, 40892; 17, C. higginsianum KACC 40807; 18, C. liliacearum KACC 40947; 19, C. lindemuthianum KACC 42433; 20, C. musae KACC 40947; 21, C. orbiculare KACC 40808; 22, C. orbiculare KACC 40903; 23, DNA mixture of C. circinans CBS 221.81 and common six molds (Alternaria sp., Aspergillus sp., Cladosporium sp., Fusarium sp., Penicillium sp., Trichoderma sp.); 24, DNA mixture of common six molds.

Fig. 4. Specificity test of the primer cirTu-F/cirTu-R set against DNAs of common six molds. M1, 1 kb DNA ladder; 1, Colletotrichum circinans CBS 125331; 2, C. circinans CBS 221.81; 3-6, C. acutatum KACC 40805, 43124, 44886, 44887; 7, C. boninense KACC 40893; 8, C. capsica KACC 46159; 9, C. caudatum KACC 41028; 10, 11, C. coccodes KACC 40227, 40808; 12, C. dematium KACC 40013; 13-16, C. gloeosporioides KACC 40003, 40448, 40690, 40892; 17, C. higginsianum KACC 40807; 18, C. liliacearum KACC 40947; 19, C. lindemuthianum KACC 42433; 20, C. musae KACC 40947; 21, C. orbiculare KACC 40808; 22, C. orbiculare KACC 40903; 23, DNA mixture of C. circinans CBS 221.81 and common six molds (Alternaria sp., Aspergillus sp., Cladosporium sp., Fusarium sp., Penicillium sp., Trichoderma sp.); 24, DNA mixture of common six molds; M2, 100 bp DNA ladder.
일반 PCR 방법과 real-time PCR 방법의 검출 감도 평가
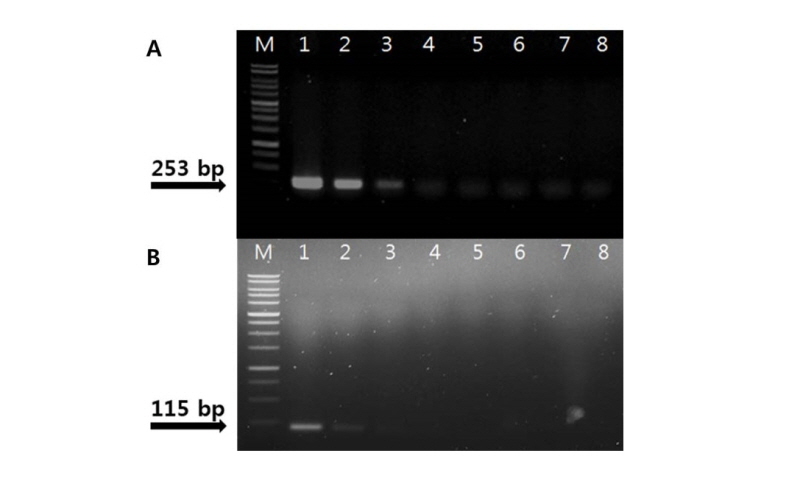
C. cirninans DNA 10 ng, 1 ng, 100 pg, 10 pg, 1 pg, 100 fg, 10 fg, 1 fg의 농도로 일반적인 PCR을 수행한 결과 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set와 cirTu-F/cirTu-R set의 검출 감도는 각각 100 pg 과 1 ng으로 확인 되었다(Fig. 5). Real-time PCR 방법으로는 Threshold cycle (Ct) 값은 거의 동일하게 나타났으며 반응산물을 모니터링한 결과 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set는 10 pg 수준까지, cirTu-F/cirTu-R set는 100 pg 수준까지 30 회 이내에 peak을 확인하였다(Fig. 6). 산출된 표준 곡선의 PCR efficiency는 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set와 cirTu-F/cirTu-R set 각각 104.4%와 103.8%, 기울기는 -3.221과 - 3.235이고 상관계수 R2 값은 0.998과 0.999로 수행한 real-time PCR 방법은 신뢰도가 높은 수준임을 나타낸다.
C. circinans에 감염된 종자에서 검출 확인
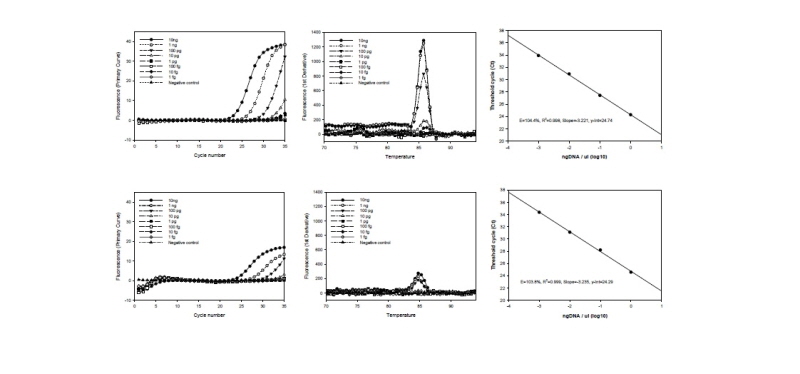
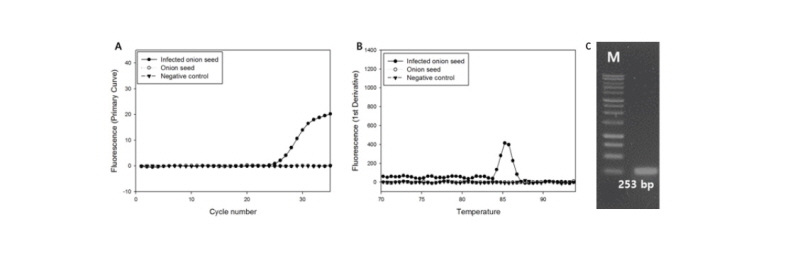
C. circinans에 감염된 양파 종자를 선별하여 DNA를 추출하고 일반 PCR과 real-time PCR 방법으로 C. circinans 검출이 가능한지 확인하였다. 검출 민감도가 더 높았던 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set를 사용하였고 일반 PCR의 경우 target band인 253 bp에서 band가 나타났고 이것으로 보아 감염된 종자에서 검출이 가능하였다(Fig. 7). 그리고 real-time PCR 방법에서도 위의 결과에 같이 melting peak가 나타나 동일하게 증폭되는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 8). 이러한 결과는 제작한 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set가 일반 PCR 방법과 real-time PCR 방법 두 가지 모두 C. circinans가 감염된 종자에서 C. circinans를 검출할 수 있다는 것을 보여준다.
최근 계통학적 연구를 통해 Colletotrichum속은 복잡한 complex를 구성을 하고 있다[14]. 총 9 개의 complex를 구성하고 있으며 C. dematium, C. lineola, C. fucti, C. anthrisci, C. spinaciae, C. circinans는 C. dematium complex group에 속하고 있다. 본 연구에는 C. dematium종만 포함이 되어있고 나머지 종들은 함께 실험하고자 하였으나 Colletotrichum종들은 대부분이 국내외로 검역대상 균주이기에 분양에 어려움이 있다. 그러므로 C. lineola, C. fucti, C. anthrisci, C. spinaciae는 tef1-α 유전자와 β-tubulin 유전자 염기서열을 제작한 특이 검출 마커와 비교하였다. tef1-α 유전자는 NCBI database에 등록된 염기서열이 거의 없어 분석이 어려웠고 β-tubulin 유전자 염기서열을 NCBI database에서 받아 비교 분석하였다. C. lineola, C. fucti, C. anthrisci는 C. circinans와 염기서열 차이가 많이 나타났고 C. spinaciae는 상동성이 높았다. 하지만 제작된 특이 검출 마커 염기서열 부분에서는 forward와 reverse에서 각각 2 개의 base의 차이가 나타나 C. circinans만 특이적으로 검출될 가능성이 높다. 향후 C. spinaciae를 포함하여 C. lineola, C. fucti, C. anthrisci는 제작된 특이 검출 마커로 PCR을 수행하여 확인하여야 할 것이다.
본 연구는 tef1-α 유전자와 β-tubulin 유전자를 타겟으로 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set와 cirTu-F/cirTu-R set를 제작하여 Colletotrichum종뿐만 아니라 부생균으로 흔하게 존재하는 6 개 속의 곰팡이에 대해서도 특이적으로 C. circinans가 검출이 가능하였다. 그리고 PCR 증폭 산물의 크기가 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set는 253 bp이고 cirTu-F/cirTu-R set는 115 bp로 작기에 PCR 반응 시간도 단축시킬 수 있어 검출 시간을 더욱 절약할 수 있다. 또한 감염된 종자에서도 검출이 가능하였기에 국내외로 채소 및 채소 종자를 수입 또는 수출할 때 C. circinans 감염 여부를 신속하게 파악하여 식물검역 작업을 단축시킬 수 있을 것으로 생각된다.
적요
탄저병균인 Colletotrichum circinans는 세계적으로 양파에 심각한 피해를 주는 병원균이다. 본 연구에서는 일반 PCR 방법과 real-time PCR 방법으로 C. circinan를 정확하면서도 쉽고 빠르게 검출이 가능한 특이 마커를 개발하였다. tef-1α 유전자와 β-tubulin 유전자를 분석하여 C. circinan를 특이적으로 검출할 수 있는 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set와 cirTu-F/cirTu-R set를 제작하였다. 일반 PCR 방법으로 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set는 100 pg, cirTu-F/cirTu-R set는 1 ng까지 검출이 가능하였고 real-time PCR 방법으로는 각각 10 pg, 100 pg까지 검출이 가능하였다. C. circinans에 인공적으로 감염된 양파 종자에서도 cirTef-F/cirTef-R set를 사용하여 일반 PCR 방법과 real-time PCR 방법 모두 C. circinans 검출이 가능하였다. 본 연구에서 개발한 C. circinans 특이 검출 마커는 수출입 되는 채소 및 종자에서 빠르고 정확하게 탄저병균인 C. circinans를 검출하는데 사용될 수 있을 것이다.