Abstract
Truffles are ectomycorrhizal fungi that belong to the genus Tuber. They exhibit symbiotic relationships, particularly with oak (Quercus spp.) and hazel (Corylus spp.) trees. We performed an inoculation using a spore suspension to synthesize mycorrhizae between European truffles,
Figures & Tables
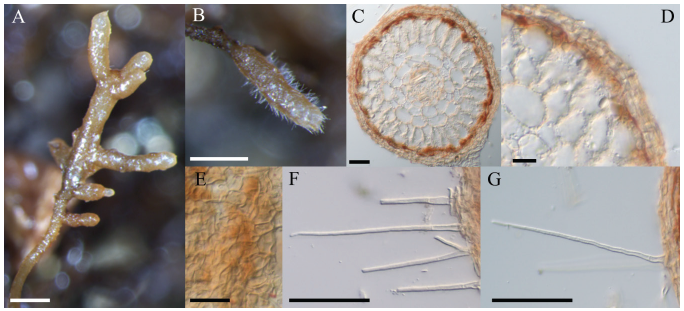
Fig. 1. Macro-morphological and anatomical characteristics of ectomycorrhizal roots of inoculated with . Mycorrhizal root tips (A, B); cross-section of mycorrhizal root tips (C, D); outer mantle surface structure (E); and separate hyphae emanating from outer mantle layer (F, G) (scale bars: A, B=500 μm; C-E=20 μm; F, G=50 μm).


