Abstract
This study was conducted to identify yeast species isolated from domestic pear blossom through gene sequencing and analysis of morphological characteristics, and to confirm specific yeast species inhibitory effects toward fire blight in immature apples, pears, and crab apple blossoms. Yeast morphological characteristics were consistent with the known characteristics of
Figures & Tables
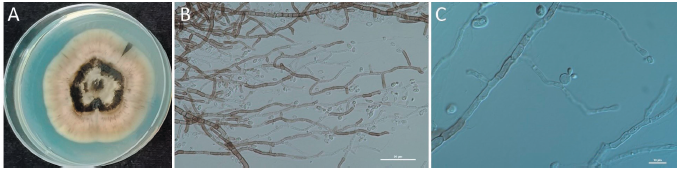
Fig. 1. Morphological characteristics of MHAU2101. Colony of the yeast isolate grown for 14 days on potato dextrose agar medium (A), melanised hyphae and conidia, scale bar=50 μm (B), production of blastospores from the swollen cell, scale bar=10 μm (C).


