Abstract
In July 2021, we surveyed diseases affecting wild vegetables grown in Hongcheon, Gangwon Province, Korea. During this survey, we observed severe seedling rot symptoms in Kamchatka goatsbeard (
Figures & Tables
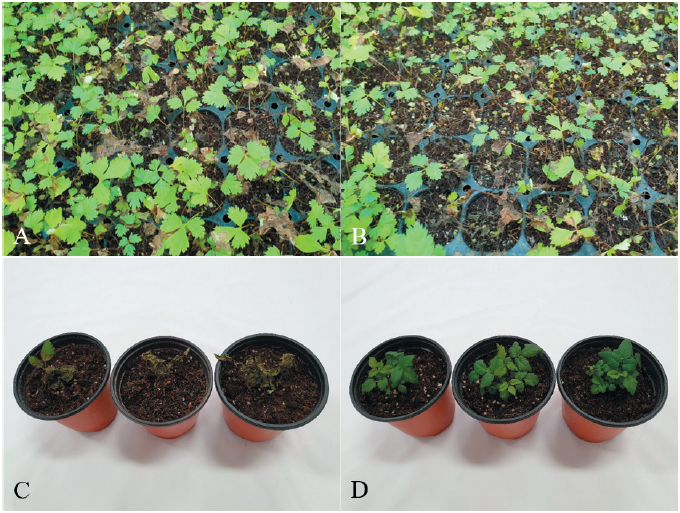
Fig. 1. Seedling rot of Kamchatka goatsbeard. (A, B) Symptoms observed in a vinyl greenhouse. (C) Symptoms induced by artificial inoculation tests with Rhizoctonia solani AG-1(IB) isolates. (D) Noninoculated seedlings (control).


