Tausonia 속 및 Apiotrichum 속은 담자균문에 속하는 효모이다. Tausonia 속은 Agaricomycotina; Tremellomycetes; Mrakiaceae에 속하며 현재까지 알려진 종은 T. pullulans, T. pamirica 2개이다. T. pullulans 는 Guehomyces pullulans와 synonym 관계에 있다[1].
Apiotrichum 속은 Trichosporonaceae에 속하는 속으로서, Apiotrichum porosum이Trichosporon 속으로 재지정되었다가[2] Liu 등[3]에 의해 다시 사용되었다. Apiotrichum 속은 자연에서 널리 분포되어 있으며, 24개 종이 속해 있다. A. dulcitum, A . laibachii, A. loubieri 는 토양에서 분리되었고[4], A. domestirum, A. montevideense는 human summer-type hypersensitivity pneumonitis (SHP)을 가진 환자의 집에서 분리되었다[3]. A. akiyoshidainum, A. chiropterorum, A. coprophilum, A. otae는 박쥐의 배설물에서 분리되었다[5].
Saprochaete는 자낭균문의 Saccharomycetes에 속하는 속으로서, 토양, 비료, 과일, 유제품, 인간의 피부, 곤충 등 다양한 환경에 분포되어 있으며, 13개 종이 알려져 있다. Saprochaete 속은 Geotrichum 속과 매우 밀접하게 연관되어 있으며, S. suaveolens, S. gigas, S. ingens 및 S. clavata는 Geotrichum 속에 속하는 종과 synonym을 가진다. Saprochaete의 유성세대는 Magnusiomyces 속에 속한다. S. quercus는 루브라참나무(Quercus rubra)의 유출액에서 분리되었다[6].
본 연구에서는 국내 담수 환경에서 물과 토양을 채집하여 야생효모를 분리 및 동정하였고 이들 중 국내 미기록 효모 6종을 선별하여 종 특성을 알아보았다.
담수효모를 분리하기 위해 광주광역시와 전라남도 여수시의 담수환경에서 담수시료와 담수퇴적물을 채집하였다. 담수시료는 조사 현장에서 핸드펌프와 nitrocellulose membrane filter (pore size 0.45 μm MCE membrane, MF-Miliporetm, Burlington, MA, USA)를 이용하여 50 mL을 여과하였다. 필터의 시료가 여과된 면을 water agar (WA, 20 g/L, agar)에 부착하여 15℃에서 1일간 배양 후 membrane filter를 제거하고 실체현미경을 이용하여 발아한 포자를 배지에서 분리하여 V8 agar배지 (V8A; 8% V8 juice [v/v] and 1.5% agar [w/v] adjusted to pH 6.0 using 10 N NaOH)에 배양하였다. 채집한 토양시료는 10-3배 희석하여 streptomycin 100 ppm이 첨가된 potato dextrose agar (PDA, Difco, Detroit, MI, USA)에 도말하여 3일간 15℃에서 배양하였다. 배양된 배지에서 단포자 분리를 통하여 담수효모를 V8A 배지에 순수분리 하였다. 분리된 효모 확보를 위하여 yeast extract peptone dextrose broth (YPDB, Sigma-Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany)에 agar를 첨가한 yeast extract peptone dextrose agar (YPDA)배지에 계대배양 하였다. 분리 효모의 포자를 관찰하기 위하여 광학현미경(H550S, Nikon, Tokyo, Japan)을 이용하여 화상자료를 확보하였다.
분리된 효모의 동정을 위하여 이 균주들의 26S rDNA의 D1/D2 부위의 염기서열을 분석하였다. NL1/NL4 primer를 이용하여 염기서열을 결정한 후 NCBI의 BLAST를 사용하여 데이터베이스에 등록되어 있는 효모들과 상동성을 비교하였고 MEGA-X를 이용하여 계통수를 작성하였다[7].
환경조건에 따른 생육 특성을 조사하기 위하여 15-40℃의 6개 온도 범위와 pH 4-8의 5개 pH 범위의 YPDB, 5%와 15% NaCl (sodium chloride [w/v])을 첨가한 YPDB, 10%와 20% glucose [w/v]를 첨가한 YPDB, yeast vitamin free base (YVB, Formedium Ltd, Hustanton, England), yeast mold broth (YMB, Difco, Detroit, MI, USA), potato dextrose broth (PDB, Difco, Detroit, MI, USA) 배지를 실험에 사용하였다[8]. 각각의 배지를 125 mL 삼각플라스크에 30 mL씩 조제하여 48시간동안 250 rpm으로 진탕 배양한 후 흡광도(600 nm, microplatereader Epoch2, Bioteck, Winooski, Vermont, USA)를 측정하였다.
Taxonomy
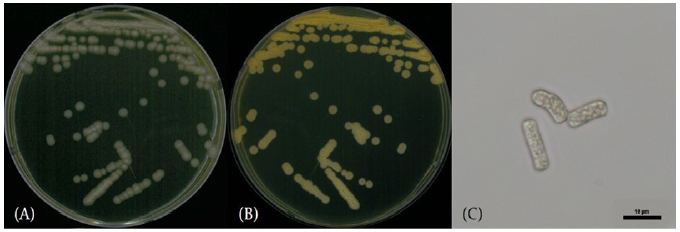
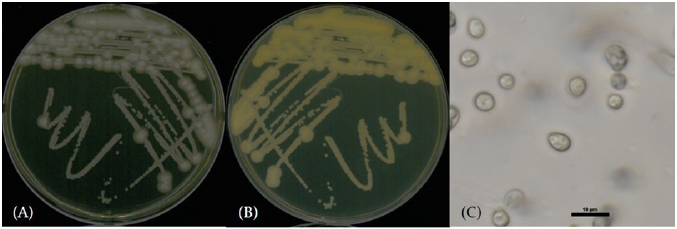
Apiotrichum chiropterorum M. Takash., Kurakado, O. Cho, K. Kikuchi, Sugiy. & Sugita [5] (Figs. 1 and 2; Table 1)
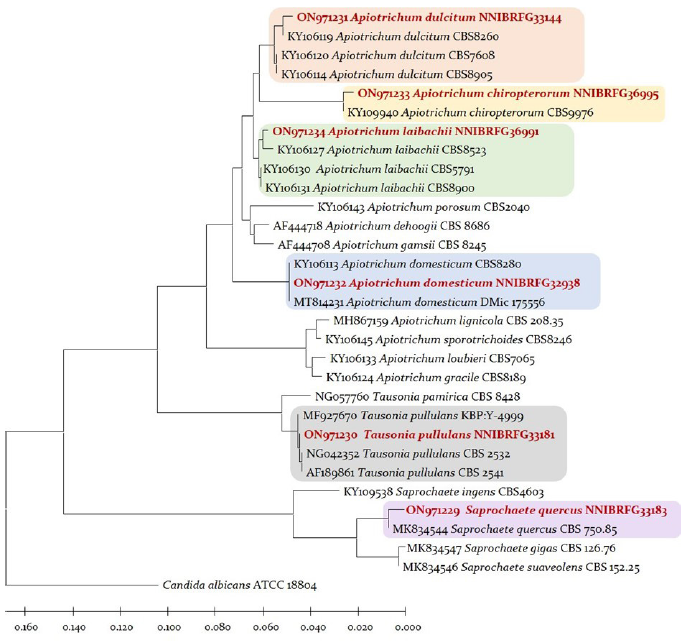
Fig. 1.Phylogenetic tree of unrecorded yeasts isolated from freshwater and related species based on a Neighbor-joining analysis of the nucleotides sequences of large subunit 26S ribosomal DNA D1/D2 region, using MEGA-X. The sequences of Candida albicans was used as outgroup. The unrecorded yeasts are shown in bold and red.
MycoBank No.: MB834542
Characterization: YPDA 배지에 획선도말하여 25℃에서 2일간 배양하였을 때 콜로니 색은 가운데부분은 노란색, 가장자리는 흰색을 띄었다. 포자의 형태는 막대형으로 자낭포자와 의균사는 관찰되지 않았다. 출아에 의한 무성생식을 하였으며, 크기는 폭 2 μm×길이 10 μm 이다. YPDB, PDB, YMB에서 생육하였고, 생육 pH는 4-8, 생육 온도는 15-30℃의 범위에서 생장하였다. Vitamin-free 배지, NaCl 및 glucose가 함유된 배지에서는 생장하지 않았다.
Habit: 하천의 담수퇴적물
Specimen examined: 광주광역시 서구 광주천, 2021.03.19., NNIBRFG36995, 국립낙동강생물자원관
Note: NNIBRFG36995 균주는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI의 blast를 이용하여 비교한 결과, A. chiropterorum CBS9976(KY109940) 균주와 100%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 같은 clade에 속하는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 A. chiropterorum으로 동정되었다.
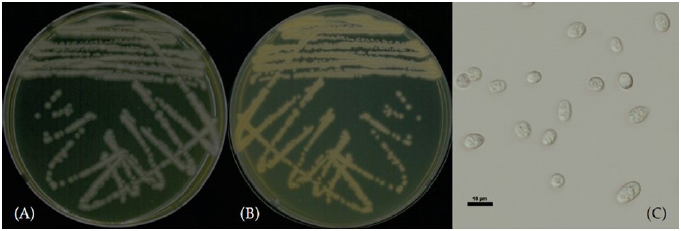
Apiotrichum domesticum (Sugita, A. Nishikawa & Shinoda) Yurkov & Boekhout [3] (Figs. 1 and 3; Table 1)
MycoBank No.: MB#834542
Characterization: YPDA 배지에 획선도말하여 25℃에서 2일간 배양하였을 때 콜로니색은 전체적으로 연한 노란빛을 띄는 흰색이었다. 포자의 형태는 타원형으로 자낭포자와 의균사는 관찰되지 않았다. 출아에 의한 무성생식을 하였으며, 크기는 폭 3-5 μm×길이 8-10 μm 이다. YPDB, PDB, YMB에서 생육하였고, 20% glucose와 5% NaCl을 함유한 YPDB에서 각각 생육하는 내당성과 내염성을 보였다. 생육 pH는 4-8, 생육 온도는 15-30℃의 범위에서 생장하였다. Vitamin-free 배지에서는 생장하지 않았다.
Habit: 하천의 여과한 물
Specimen examined: 전라남도 여수시 주삼천, 2021.03.24., NNIBRFG32938, 국립낙동강생물자원관Note: NNIBRFG32938 균주는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI의 blast를 이용하여 비교한 결과, A. domesticum CBS8280(KF036966) 균주와 100%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 A. domesticum CBS8280, A. domesticum DMic175556 균주와 같은 clade에 속하는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 A. domesticum으로 동정되었다.
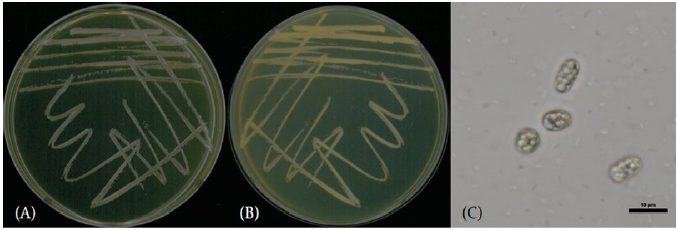
Apiotrichum dulcitum (Berkhout) Yurkov & Boekhout [3] (Figs. 1 and 4; Table 1)
MycoBank No.: MB813412
Characterization: YPDA 배지에 획선도말하여 25℃에서 2일간 배양하였을 때 콜로니는 연한 노란색을 띄었고 광택이 났다. 포자의 형태는 타원형으로 자낭포자와 의균사는 관찰되지 않았다. 출아에 의한 무성생식을 하였으며, 크기는 폭 2-3 μm×길이 8 μm 이다. YPDB, PDB, YMB에서 생육하였고, 생육 pH는 5-8, 생육 온도는 15-30℃의 범위에서 생장하였다. Vitamin-free 배지, NaCl 및 glucose가 함유된 배지에서는 생장하지 않았다.
Habit: 하천의 여과한 물
Specimen examined: 광주광역시 광산구 풍영정천, 2021.03.19., NNIBRFG33144, 국립낙동강생물자원관
Note: NNIBRFG33144 균주는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI의 blast를 이용하여 비교한 결과, A. dulcitum CBS8257 (KF036967) 균주와 99.8%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 A. dulcitum CBS8260 균주와 같은 clade에 속하는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 A. dulcitum으로 동정되었다.
Apiotrichum laibachii (Windisch) Yurkov & Boekhout [3] (Figs 1 and 5; Table 1)
MycoBank No.: MB813415
Characterization: YPDA 배지에 획선도말하여 25℃에서 2일간 배양하였을 때 콜로니는 연한 노란색을 띄었다. 포자의 형태는 둥근 원형으로 자낭포자와 의균사는 관찰되지 않았다. 출아에 의한 무성생식을 하였으며, 크기는 폭 3 μm×길이 4 μm이다. YPDB, PDB, YVB, YMB에서 생육하였고, 20% glucose와 5% NaCl을 함유한 YPDB에서 생육하는 내당성과 내염성을 보였다. 생육 pH는 4-8, 생육 온도는 15-30℃의 범위에서 생장하였다.
Habit: 하천의 여과한 물
Specimen examined: 광주광역시 서구 광주천, 2021.03.19., NNIBRFG36991, 국립낙동강생물자원관
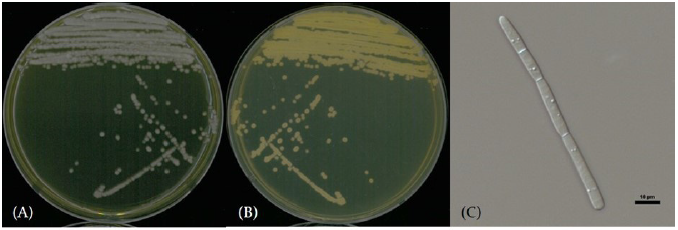
Note: NNIBRFG36991 균주는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI의 blast를 이용하여 비교한 결과, A . laibachii CBS5790(KF036976) 균주와 100%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 A . laibachii CBS8523 균주와 같은 clade에 속하는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로A . laibachii으로 동정되었다. Saprochaete quercus de Hoog & M.T. Sm [6] (Figs 1 and 6; Table 1)
MycoBank No.: MB500145
Characterization: YPDA 배지에 획선도말하여 25℃에서 2일간 배양하였을 때 콜로니는 전체적으로 흰색을 띄었다. 포자의 형태는 막대형으로 자낭포자와 의균사는 관찰되지 않았다. 출아에 의한 무성생식을 하였으며, 크기는 폭 3 μm×길이 100 μm이다. YPDB, PDB, YVB, YMB에서 생육하였고, 생육 pH는 4-8, 생육 온도는 15-30℃의 범위에서 생장하였다. 10% glucose가 포함된 배지에서는 생장하여 내당성이 있었으며, NaCl이 함유된 배지에서는 생장하지 않았다.
Habit: 하천의 여과한 물
Specimen examined: 광주광역시 서구 광주천, 2021.03.19., NNIBRFG33183, 국립낙동강생물자원관
Note: NNIBRFG33183 균주는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI의 blast를 이용하여 비교한 결과, S. quercus CBS750.85 (MK834544) 균주와 99.81%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 같은 clade에 속하는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 S. quercus으로 동정되었다.
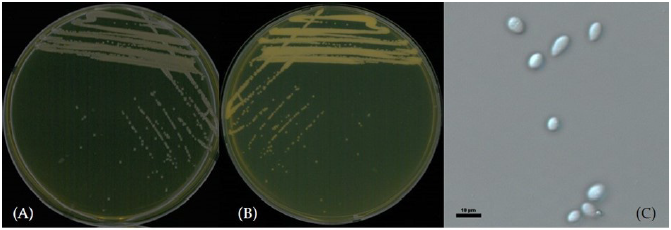
Tausonia pullulans Xin Zhan Liu, F.Y. Bai, M. Groenew & Boekhout [3] (Figs 1 and 7; Table 1)
MycoBank No.: MB#812190
Characterization: YPDA 배지에 획선도말하여 25℃에서 2일간 배양하였을 때 콜로니는 연한 노란색을 띄며 광택이 났다. 포자의 형태는 타원형으로 자낭포자와 의균사는 관찰되지 않았다. 출아에 의한 무성생식을 하였으며, 크기는 폭 2 μm×길이 3-5 μm이다. YPDB, PDB, YMB에서 생육하였고, 20% glucose를 함유한 배지에서 생육하는 내당성을 보였다. 생육 pH는 5-8, 생육 온도는 15-30℃의 범위에서 생장하였다. Vitamin-free 배지, NaCl이 함유된 배지에서는 생장하지 않았다.
Habit: 하천의 여과한 물
Specimen examined: 광주광역시 서구 광주천, 2021.03.19., NNIBRFG33181, 국립낙동강생물자원관
Note: NNIBRFG33181 균주는 26S D1/D2 영역의 염기서열을 NCBI의 blast를 이용하여 비교한 결과, T. pullulans KBP:Y-4999 (MF927670) 균주와 99.43%의 상동성을 보였으며, 계통수 상에서도 T. pullulans CBS2532, CBS2541 균주와 같은 clade에 속하는 것으로 확인되어 최종적으로 T. pullulans으로 동정되었다.
적요
본 연구는 광주광역시와 전라남도 여수시의 담수환경으로부터 야생효모를 분리하여 특성 분석을 하였다. 분리된 효모의 동정을 위하여 26S rDNA의 D1/D2부위 염기서열을 이용하였다. 결과적으로 Apiotrichum chiropterorum (NNIBRFG36995), A. domesticum (NNIBRFG32938), A. dulcitum (NNIBRFG33144), A. laibachii(NNIBRFG36991), S. quercus (NNIBRFG33183), Tausonia pullulans (NNIBRFG33181)등 6종의 야생효모들을 동정하였다. 이들 6종의 효모는 국내에 기록된 바가 없으며, 본 논문이 최초보고이다. 미기록 효모 모두 PD, YM 배지에서 잘 자랐으며, 15-30℃ 온도범위에서 생육하였다. A. domesticum (NNIBRFG32938), A . laibachii (NNIBRFG36991), Tausonia pullulans (NNIBRFG33181) 균주들은 20% glucose를 함유한 YPD 배지에서 생육하는 내당성을 보였으며 A. domesticum (NNIBRFG32938)과 A . laibachii (NNIBRFG36991)는 5% NaCl을 함유한 YPD 배지에서도 생육하여 내염성을 가졌다.