Abstract
From June to August 2021, we surveyed diseases affecting beet (
Figures & Tables
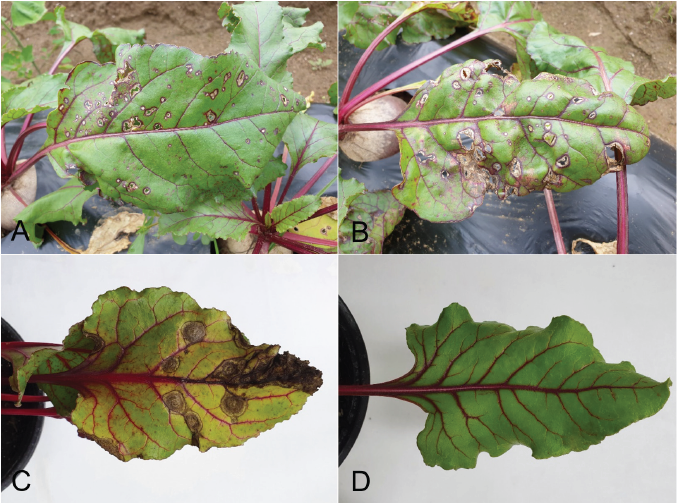
Fig. 1. Leaf spot symptoms in beet plants. A and B: Symptoms observed in the investigated fields. C: Symptoms observed in the plant artificially inoculated with a isolate in a pathogenicity test. D: A non-inoculated plant (control).


