Abstract
Fungal diseases including anthracnose, stem rot, blight, wilting, and root rot of crops are caused by phytopathogens such as
Figures & Tables
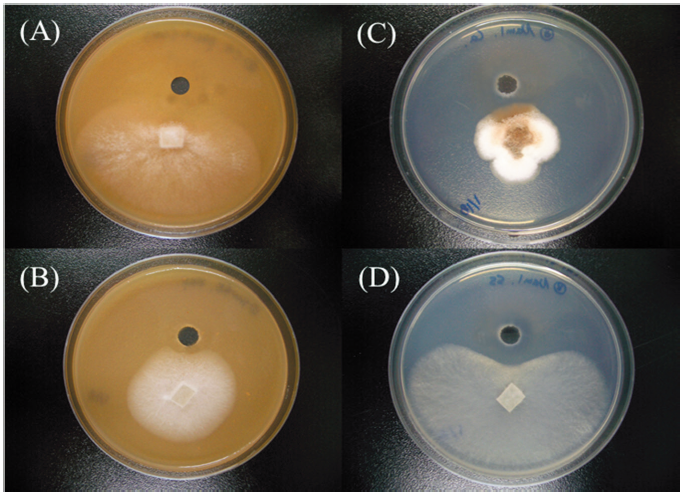
Fig. 1. Antifungal activities of SRCM 121379 against several phytopathogenic fungal strains ([A-B], colonies on V8 juice agar and [C-D], potato dextrose agar) by dual culture. subtilis SRCM 121379 against KACC 40166 (A), Fusarium solani which isolated from hydroponically cultured (B), KACC 40042 (C), and KACC 41065 (D) by agar well diffusion method


