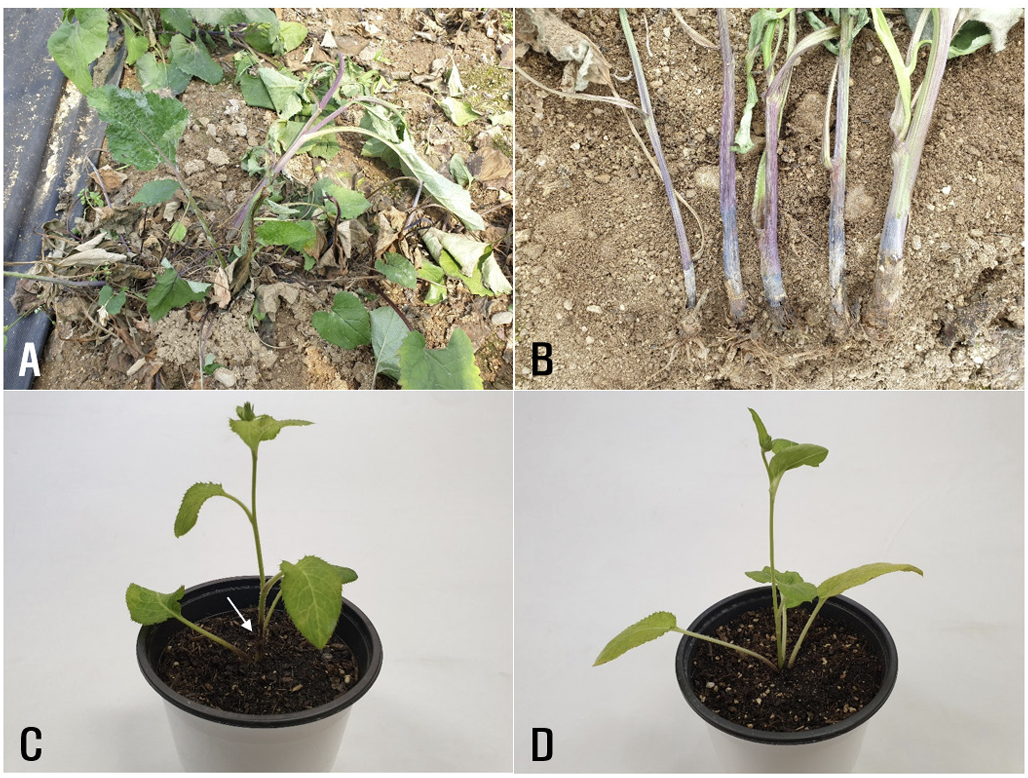
Gondre [Cirsium setidens (Dunn) Nakai], also known as Korean thistle, belongs to the family Asteraceae and is native to Korea [1]. The plant is a perennial plant that grows naturally in montane and submontane areas, that is cultivated as a wild vegetable by farmers in Korea, and its young leaves can be cooked and seasoned. In June 2022, we surveyed the disease occurrence in wild vegetables cultivated in Taebaek, Korea. During the disease survey, stem rot symptoms were observed in Gondre plants growing in a vinyl greenhouse. Symptoms formed on the stems at or above the soil line, and the rotted lesions were dark brown to black (Fig. 1A and B). Severely diseased plants were wilted and blighted. We investigated stem rot outbreaks at three sites in the vinyl greenhouse, and after studying 100 plants per site, the disease incidence among the plants ranged from 1 to 5%.
Fungal isolates were obtained from the diseased stem lesions of Gondre plants using a previously described method [2]. Three isolates (RS-2207, RS-2209, and RS-2213) of Rhizoctonia sp. from the analyzed stem lesions were examined for morphological characteristics using a compound microscope (Nikon Eclipse Ci-L, Japan). Hyphae branched near the distal septa of the hyphal cells and were constricted at the points of hyphal branches. Hyphal septa were formed at a short distance from the points of the hyphal branches. These isolates did not produce conidia and clamp connections on the hyphae. The isolates were identified as Rhizoctonia solani Kühn, as per previous morphological descriptions [3,4].
R. solani isolates were tested for the identification of anastomosis groups using tester isolates of R. solani
Fig. 1
Stem rot symptoms of Gondre plants. (A and B) Symptoms observed in the vinyl greenhouse. (C) Symptoms induced by artificial inoculation test with Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-2(IV) RS-2209. The white arrow indicates the lesion formed on the stem. (D) A non-inoculated plant (control).

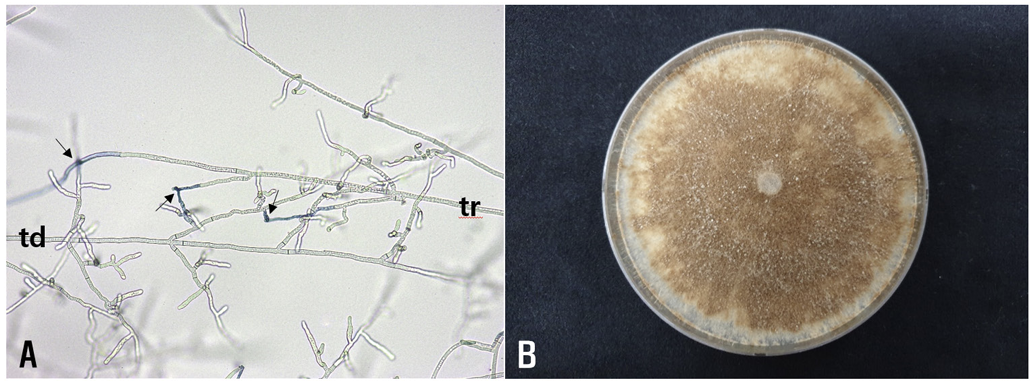
(AG-1 through AG-5) as previously described [5,6]. All the tested isolates were classified as R. solani AG2-2. The anastomosis reactions between the tested and tester isolates are shown in Fig. 2A. Colonies of the isolates cultured on potato dextrose agar (PDA) were light to dark brown in color (Fig. 2B). Sclerotia were absent or rarely formed on the medium. The isolates did not grow on PDA at 35°C. The cultural characteristics of the isolates were similar to those of the R. solani type IV cultures, which were described in a previous study [7].
To validate the identification results obtained via the morphological and cultural characteristics, and the results of the anastomosis tests, a phylogenetic analysis was conducted. The DNA templates of the three isolates were extracted using a previously described method [8], with slight modifications. Internal transcribed spacer regions 1 & 2 and intervening 5.8S nrDNA (ITS) were investigated using primers ITS1 and ITS4 [9]. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification was performed using the DNA FreeMultiplex Master Mix (Cellsafe, Korea) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The amplifying condition included an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 sec, annealing at 55 °C for 60 sec, extension at 72 °C for 30 sec, and a final extension at 72 °C for 10 min. The PCR products were purified using a Universal DNA Purification Kit (Tiangen, China) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Purified PCR products were sequenced at Bionics (Seoul, Korea). The obtained sequences were aligned using MUSCLE [10] and modified, when necessary, using MEGA 7 software [11].
Fig. 2
Anastomosis test and cultural appearance of Rhizoctonia solani RS-2209 from Gondre plants. (A) Anastomosis reactions between the tested isolate (td) and the tester isolate (tr) of R. solani AG-22(IV) observed using a compound microscope. The arrows indicate points of hyphal anastomosis. (B) A colony of the isolate grown on potato dextrose agar at 25℃ for 10 days.
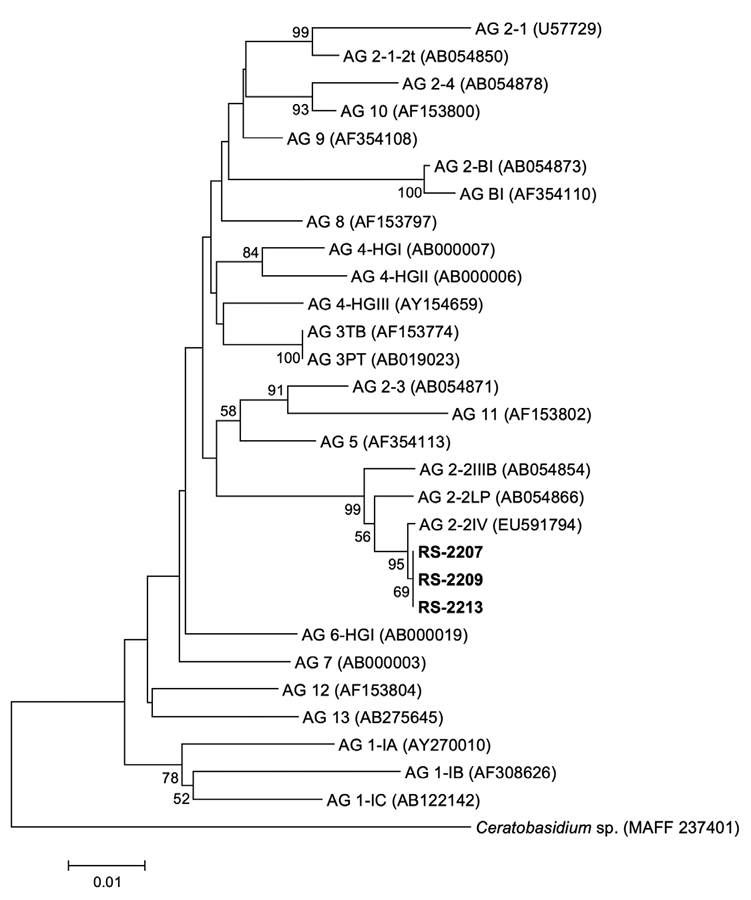
A phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method with the maximum composite likelihood model, and 1,000 bootstrap replicates were performed. Ceratobasidium sp. (MAFF 237401) was used as an outgroup taxon. Sequence data of reference strains were obtained from the previous studies and NARO Genebank [12-24]. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that all the isolates were R. solani AG-2-2(IV) (Fig. 3). The nucleotide sequences of the three isolates were deposited in the NCBI GenBank under the accession numbers OQ991158– OQ991160.
Three isolates of R. solani AG-2-2(IV) were tested for pathogenicity to Gondre plants using an artificial inoculation test. Mycelial disks (10 mm in diameter) cut from the margins of actively growing cultures of each isolate on PDA were placed on the stems at the soil surface level of 5-month-old Gondre plants grown in circular plastic pots (height: 13.5 cm; upper diameter: 15 cm; lower diameter: 10 cm) in a vinyl greenhouse. Inoculated plant pots were placed in plastic boxes (72 cm × 54 cm × 45 cm) under 100% relative humidity at room temperature (24�28°C) for 7 days. Thereafter, the inoculated plant pots were taken out of the plastic boxes and kept under alternating cycles of 12 hr LED (light emitting diode) light and 12 hr darkness in a cultivation room at 24�28°C for 5 days. The inoculation test was carried out three times. The results of pathogenicity tests were checked for induced stem rot symptoms 12 days after inoculation. All the tested isolates induced stem rot symptoms in the inoculated plants (Fig. 1C), but no symptoms were observed in the control plants (Fig. 1D). The lesions induced by the inoculation test were similar to those observed in the vinyl greenhouse investigated during the survey. Furthermore, inoculated isolates were successfully detected in these lesions.
Several diseases, including powdery mildew and rust, have been reported in Gondre [25]. However, no prior reports of diseases caused by R. solani on this plant were noted. R. solani AG-2-2(IV) is known to cause stem rot in Angelica jaluana Nakai and Gypsophila elegans M. Bieb. in Korea [26,27]. Here, we report a case of R. solani AG-2-2(IV) causing stem rot in Gondre.
Fig. 3
Phylogenetic tree based on the sequences of internal transcribed spacer regions 1 & 2 and intervening 5.8S nrDNA of the three isolates (RS-2207, RS-2209, and RS-2213) from Gondre plants and reference strains. The reference sequence data were obtained from the NCBI GenBank database. The tree was generated using the neighbor-joining method with the maximum composite likelihood model in MEGA version 7 software. The bootstrap support values ≥50 are shown at the nodes. The scale bar represents the number of nucleotide substitutions per site.